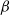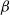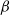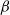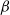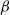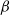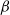1777 results
P.022 Gender disparity in canadian institutes of health research funding within neurology
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.147 The growing problem of spine surgery wait times in British Columbia: longitudinal trends and impacts on perioperative outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
GR.6 Meningioma molecular classification predicts response to surgery and adjuvant radiotherapy: an integrated clinicomolecular analysis & prospective validation
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
B.6 Long-term risk of subsequent stroke after transient ischemic attack or minor stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
GR.5 Establishing the utility of multi-platform liquid biopsy by integrating the CSF methylome and proteome in CNS malignancy
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
F.3 Multicentre prospective validation of integrated molecular classification of meningiomas and prediction of recurrence risk using DNA methylation
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, pp. S12-S13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
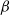 $\beta$-wave-based exploration of sensitive EEG features and classification of situation awareness
$\beta$-wave-based exploration of sensitive EEG features and classification of situation awareness
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nondigestible carbohydrates and gut microbiota: A dynamic duo in host defense
-
- Journal:
- Animal Nutriomics / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Toward standardization, harmonization, and integration of social determinants of health data: A Texas Clinical and Translational Science Award institutions collaboration – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lepidocrocite in a Calcareous, Well-Drained Soil
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 30 / Issue 5 / October 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 394-396
-
- Article
- Export citation
Catalysis of Nontronite in Phenols and Glycine Transformations
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 39 / Issue 2 / April 1991
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 202-210
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pyrogallol Transformations as Catalyzed by Nontronite, Bentonite, and Kaolinite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 37 / Issue 6 / December 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 525-531
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of a syndrome-based stewardship intervention on antipseudomonal beta-lactam use, antimicrobial resistance, C. difficile rates, and cost in a safety-net community hospital
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dinocephalosaurus orientalis Li, 2003: a remarkable marine archosauromorph from the Middle Triassic of southwestern China
-
- Journal:
- Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of The Royal Society of Edinburgh , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, pp. 1-33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MODIS land surface temperature in East Antarctica: accuracy and its main affecting factors
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contract noncompliance in agricultural conservation programs: Panel evidence from Louisiana, USA
-
- Journal:
- Agricultural and Resource Economics Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Toward standardization, harmonization, and integration of social determinants of health data: A Texas Clinical and Translational Science Award institutions collaboration
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Voltage-gated sodium channel gene mutation and P450 gene expression are associated with the resistance of Aphis spiraecola Patch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to lambda-cyhalothrin
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 49-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Functional neuroimaging biomarkers of anhedonia response to escitalopram plus adjunct aripiprazole treatment for major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Crystallization between (100) Goethite and (001) Orientation of Hematite – A Review
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 242-251
-
- Article
- Export citation