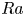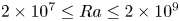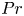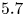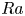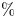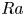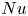207 results
Impact of total parenteral nutrition versus exclusive enteral nutrition on postoperative adverse outcomes in patients with penetrating Crohn’s disease undergoing surgical resection: A retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2024, pp. 1-28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Early Holocene exploitation of taro and yam among southern East Asian hunter-gatherers
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The long-term spatio-temporal trends in burden and attributable risk factors of major depressive disorder at global, regional and national levels during 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for GBD 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2024, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A 1179-yr (417–1595 CE) tree-ring oxygen isotope chronology for northern Japan validated using the 774–775 CE radiocarbon spike
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of partial wetting by CMAS droplets using multiphase many-body dissipative particle dynamics and data-driven discovery based on PINNs
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 985 / 25 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, A7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhanced heat transfer and reduced flow reversals in turbulent thermal convection with an obstructed centre
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 981 / 25 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inverse association between maternal serum concentrations of trace elements and risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case–control study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1425-1435
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association between the PLTP rs4810479 SNP and Serum Lipid Traits in the Chinese Maonan and Han Populations
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis of Monozygotic Twin Discordant for Double Outlet Right Ventricle
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 370-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between micronutrients intake and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 12 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, e117
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Operational Dilemmas and Cadre Education and Training at a County Party School in China
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 258 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 513-528
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Lift generation mechanism of the leading-edge vortex for an unsteady plate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, A30
-
- Article
- Export citation
A 24-year longitudinal study of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from patients with bacteraemia and urinary tract infections reveals the association between capsular serotypes, antibiotic resistance, and virulence gene distribution
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, e155
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Measurements of plasma density profile evolutions with a channel-guided laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2023, e85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Utilisation Rate of Clozapine for Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia Within Trustwide Adult Inpatient Services Over One Year
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue S1 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 July 2023, p. S189
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
364 Beneficial Actions of SGLT2 Inhibition and H2S Therapy in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, p. 108
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation