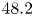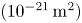235 results
Translating impartiality into operations from a financial perspective: Uncertainties and solutions
-
- Journal:
- International Review of the Red Cross , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, pp. 1-37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anaesthesia management of interventional cardiac catheterisation for pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum and critical pulmonary stenosis: a retrospective analysis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Instability of a weakly viscoelastic film flow on an oscillating inclined plane
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, A36
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transition induced by a bursting vortex ring in channel flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 986 / 10 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2024, A11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in several regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mediterranean diet for cardiovascular disease: an evidence mapping study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e118
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The small heat shock protein Hsp20.8 imparts tolerance to high temperatures in the leafminer fly, Liriomyza trifolii (Diptera: Agtomyzidae)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, pp. 230-236
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identification of Potential Biomarkers of Septic Shock Based on Pathway and Transcriptome Analyses of Immune-Related Genes
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An Evaluation of the Supplementation of Dietary-Modified Palygorskite on Growth Performance, Zearalenone Residue, Serum Metabolites, and Antioxidant Capacities in Broilers Fed a Zearalenone-Contaminated Diet
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 6 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 474-484
-
- Article
- Export citation
The origins of saddles and riding technology in East Asia: discoveries from the Mongolian Altai
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reevaluation of the protein requirement in Chinese elderly adults without sarcopenia with the indicator amino acid oxidation technique
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1377-1383
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
How Do Risk Preferences Affect Golf Course Superintendents’ Adoption of Precision Irrigation Technologies? Implications from Prospect Theory – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics / Volume 56 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2023, p. 184
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of phase-adjusted interventions for COVID-19 using an improved SEIR model
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dual-tunable phononic waveguides for manipulation of guided Lamb waves
-
- Journal:
- Programmable Materials / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comprehensive psychological crisis intervention of college students with anxiety disorder
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Instability of a viscoelastic film with insoluble surfactants on an oscillating plane
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, A39
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inertial solution for high-pressure-difference pulse-decay measurement through microporous media
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2023, R1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Zoonotic pathogens identified in rodents and shrews from four provinces, China, 2015–2022
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, e174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
How Do Risk Preferences Affect Golf Course Superintendents’ Adoption of Precision Irrigation Technologies? Implications from Prospect Theory
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics / Volume 55 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2023, pp. 516-535
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation