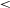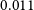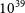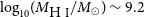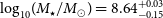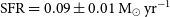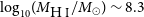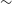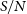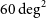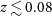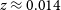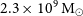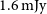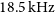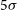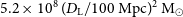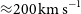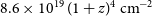468 results
Characteristics of healthcare personnel with SARS-CoV-2 infection: 10 emerging infections program sites in the United States, April 2020–December 2021
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mechanically induced localisation of SECONDARY WALL INTERACTING bZIP is associated with thigmomorphogenic and secondary cell wall gene expression
-
- Journal:
- Quantitative Plant Biology / Volume 5 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2024, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incidence of mental health diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multinational network study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations between food insecurity and diabetes risk factors in US adolescents in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007–2016
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, e68
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nation-Wide Variation in Presence of Legislation or Protocols for EMS Care of Operational Canines
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2024, pp. 59-64
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
93 Impact of Cardiovascular Risk on Cognitive and Brain Aging in Autosomal Dominant Frontotemporal Dementia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 193-194
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
5 Rejuvenating Blood Factor TIMP2 Relates to Physical Activity and Cognitive Functioning in Older Adults on The Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 106-107
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
32 Prediction of Seizure Outcome with Presurgical IAT, MRI, and PET in Patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Undergoing Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 31-32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The predictive validity of the strange situation procedure: Evidence from registered analyses of two landmark longitudinal studies
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2023, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Excessive fear of clusters of holes, its interaction with stressful life events and the association with anxiety and depressive symptoms: large epidemiological study of young people in Hong Kong
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, e151
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The evolving role of data & safety monitoring boards for real-world clinical trials
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, e179
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Systematic Review on the Mechanisms of Action of Psilocybin in the Treatment of Depression
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S416-S417
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The host galaxy of FRB 20171020A revisited
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2023, e029
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: The diversity of HI structural parameters in nearby galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e032
-
- Article
- Export citation
Estimating the prognostic value of cross-sectional network connectivity for treatment response in depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2023, pp. 317-326
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Validation of magnetized gas-jet experiments to investigate the effects of an external magnetic field on laser-plasma instabilities
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2023, 175890201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Childhood adversities and risk of posttraumatic stress disorder and major depression following a motor vehicle collision in adulthood
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2023, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY Pilot Survey: Public release of HI kinematic models for more than 100 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e059
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sex differences in regional gray matter density in pre-adolescent binge eating disorder: a voxel-based morphometry study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 13 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 6077-6089
-
- Article
- Export citation