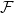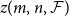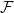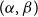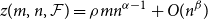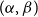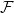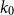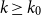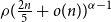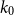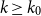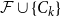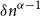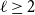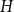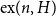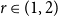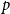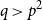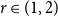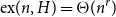85 results
Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Disease Burden attributable to High Body Mass Index in Belt and Road Initiative Countries, 1990-2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2024, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Migration of confined micro-swimmers subject to anisotropic diffusion
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 985 / 25 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, A44
-
- Article
- Export citation
Investigation of fermentation profiles, bacterial community structure and bacterial β-carotene synthesis of alfalfa silage treated with propionic acid or its combination with squalene
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Trauma diagnostic-related target proteins and their detection techniques
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reflections on resilience
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Deep learning-based companion robot on senile dementia patients
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Treatment experience with and clinicopathological analysis of vocal fold leukoplakia per appearance classification guidance: a cohort of 1442 patients
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2023, pp. 461-465
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
RNA N6-methyladenosine of DHAPAT and PAP involves in regulation of diapause of Bombyx mori via the lipid metabolism pathway
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. 665-675
-
- Article
- Export citation
Resilience in children with chronic illness: Tests of the shift-and-persist and skin-deep resilience theories
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 5 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 June 2023, pp. 2264-2274
-
- Article
- Export citation
Weight self-misperception and obesity-related knowledge, attitudes, lifestyle behaviours and cardio-metabolic markers among Chinese school-aged children and adolescents
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 1549-1561
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Efficacy of dynamic interpersonal therapy for major depressive disorder in China: results of a multicentered, three-arm, randomized, controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 15 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, pp. 7242-7254
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bipartite-ness under smooth conditions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 February 2023, pp. 546-558
-
- Article
- Export citation
Waiting is painful: The impact of anticipated dread on negative discounting in the loss domain
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 17 / Issue 6 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 1353-1378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparing mixed intertemporal tradeoffs with pure gains or pure losses
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 16 / Issue 3 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 709-728
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Many Turán exponents via subdivisions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2022, pp. 134-150
-
- Article
- Export citation
Slices of parameter space for meromorphic maps with two asymptotic values
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2021, pp. 99-139
- Print publication:
- January 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Comparison of Preterm Birth Rate and Growth from Birth to 18 Years Old between in Vitro Fertilization and Spontaneous Conception of Twins
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2021, pp. 228-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
On Turán exponents of bipartite graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 2 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2021, pp. 333-344
-
- Article
- Export citation
Recovering Chemistry at Atomic Resolution using Multi-Modal Spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 1226-1228
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dietary patterns and their associations with the metabolic syndrome and predicted 10-year risk of CVD in northwest Chinese adults
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2020, pp. 913-922
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation