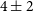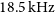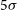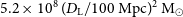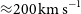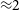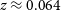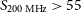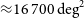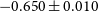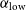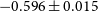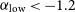278 results
The predictive role of symptoms in COVID-19 diagnostic models: A longitudinal insight
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Turbulence mitigation in maximum-J stellarators with electron-density gradient – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, 945900101
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Increasing the equitability of data citation in paleontology: capacity building for the big data future
-
- Journal:
- Paleobiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey III: Spectra and Polarisation In Cutouts of Extragalactic Sources (SPICE-RACS) first data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2023, e040
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Agricultural Research Service Weed Science Research: Past, Present, and Future
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2023, pp. 312-327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A longitudinal comparison of emotional, behavioral and attention problems in autistic and typically developing children
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 16 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2023, pp. 7707-7719
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: The diversity of HI structural parameters in nearby galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e032
-
- Article
- Export citation
WALLABY Pilot Survey: Public release of HI kinematic models for more than 100 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e059
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The First Large Absorption Survey in H i (FLASH): I. Science goals and survey design
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2022, e010
-
- Article
- Export citation
Externalizing behavior in preschool children in a South African birth cohort: Predictive pathways in a high-risk context
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2022, pp. 982-999
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Occupational risk factors for severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection among healthcare personnel: A 6-month prospective analysis of the COVID-19 Prevention in Emory Healthcare Personnel (COPE) Study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2022, pp. 1664-1671
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Turbulence mitigation in maximum-J stellarators with electron-density gradient
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 88 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2022, 905880112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Implementation of SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody Infusion Sites at Three Medical Centers in the United States: Strengths and Challenges Assessment to Inform COVID-19 Pandemic and Future Public Health Emergency Use
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2022, e112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Implications of new technologies for future food supply systems
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 159 / Issue 5-6 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2021, pp. 315-319
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The GLEAM 200-MHz local radio luminosity function for AGN and star-forming galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2021, e041
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cardiac echocardiogram findings of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2-associated multi-system inflammatory syndrome in children – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2021, p. 727
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cardiac echocardiogram findings of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2-associated multi-system inflammatory syndrome in children
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2021, pp. 718-726
-
- Article
- Export citation
Phase contrast imaging measurements and numerical simulations of turbulent density fluctuations in gas-fuelled ECRH discharges in Wendelstein 7-X
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 87 / Issue 3 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2021, 905870314
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation