205 results
The effect of psychiatric decision unit services on inpatient admissions and mental health presentations in emergency departments: an interrupted time series analysis from two cities and one rural area in England – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effect of psychiatric decision unit services on inpatient admissions and mental health presentations in emergency departments: an interrupted time series analysis from two cities and one rural area in England
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Validation of the Passive Surveillance Stroke Severity Score in Three Canadian Provinces
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of universal chlorhexidine bathing with or without COVID-19 intensive training on staff and resident COVID-19 case rates in nursing homes
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assessing past versus present severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection: A survey of criteria for discontinuing precautions in asymptomatic patients testing positive on admission
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 237-240
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
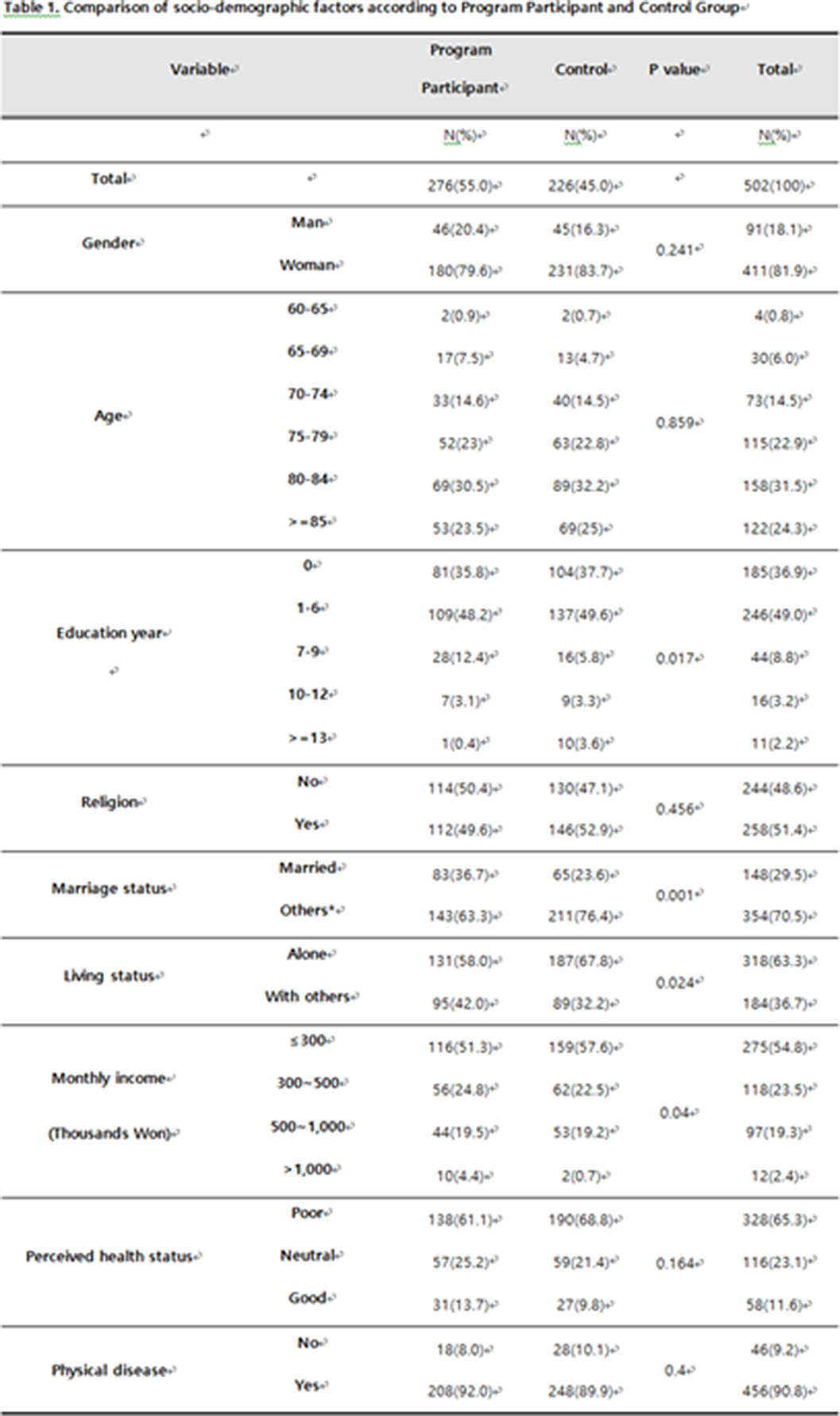
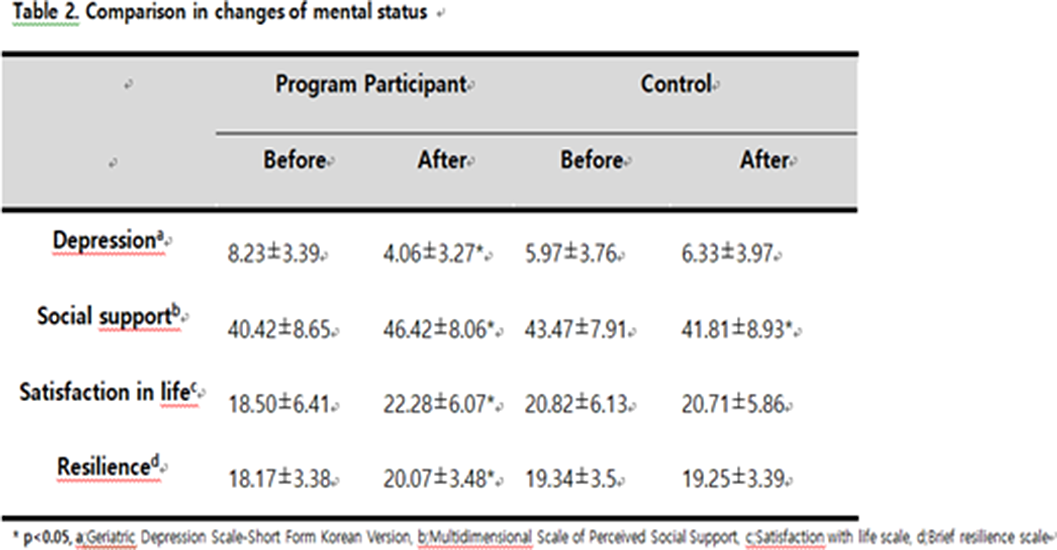
The effect of suicide prevention program for community dwelling elderly
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S367-S368
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Self-compassion is associated with the superior longitudinal fasciculus in the mirroring network in healthy individuals
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S550
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Incidence and risk factors for clinically confirmed secondary bacterial infections in patients hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, pp. 1650-1656
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
481 Interactions between buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 139-140
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Transportation and language access as crucial pillars for an immigrant-inclusive 21st-century food security program
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, pp. 1925-1929
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On-site food provision in early childhood education services in Victoria, Australia
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, E171
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Immunogenicity and safety of a quadrivalent meningococcal tetanus toxoid-conjugate vaccine administered concomitantly with other paediatric vaccines in toddlers: a phase III randomised study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2021, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Parity and the risk of incident dementia: a COSMIC study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 29 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2020, e176
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparison of patulous Eustachian tube patients with and without a concave defect in the anterolateral wall of the tubal valve
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 134 / Issue 6 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 June 2020, pp. 526-532
- Print publication:
- June 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Framingham risk score is associated with hearing outcomes in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 134 / Issue 5 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2020, pp. 419-423
- Print publication:
- May 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-mediated LTD Involves two Interacting Ca2+ Sensors, NCS-1 and PICK1
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 24 / Issue S1 / January 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, 24-E84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P0166 - Effect of Buspirone, a Serotonin partial agonist, on cognitive function in schizophrenia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 23 / Issue S2 / April 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. S241
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Prevalence and Its Correlates of Night Eating Syndrome in Schizophrenic Outpatients
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 30 / Issue S1 / March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The state of the art in European research on reducing social exclusion and stigma related to mental health: A systematic mapping of the literature
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 29 / Issue 6 / August 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 381-389
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prevalence and Its Correlates of Restless Legs Syndrome in Outpatients with Bipolar Disorders
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 30 / Issue S1 / March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation