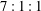26 results
F.3 Comprehensive multiplatform analysis of CDKN2A alterations in meningiomas
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Superior semicircular canal dehiscence repair with small middle fossa craniotomy using an oto-microscopic and co-endoscopic assisted approach
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 136 / Issue 6 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, pp. 559-561
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary digital tools to support self-management of gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic literature review
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 80 / Issue OCE5 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2021, E221
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydrodynamical Simulations of Misaligned Accretion Discs in Binary Systems: Companions tear discs
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 16 / Issue S362 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2023, pp. 177-183
- Print publication:
- June 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
P03-141 - The Sleep and Quality of Life in Schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 25 / Issue S1 / 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2020, 25-E1110
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P01-309 - The Life Quality of the Receivers a Year After Renal Transplantation
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 25 / Issue S1 / 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2020, 25-E517
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P01-310 - Fatigue, Anxiety and Depression in Cancer Patients
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 25 / Issue S1 / 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2020, 25-E518
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effects of Two Types of Calorie Restriction on Methylation Levels of Adiponectin Receptor 1 (AdipoR1) and Leptin Receptor Overlapping Transcript (Leprot) in a MMTV-TGF-α Breast Cancer Mouse Model – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 123 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2020, p. 1079
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Red–green–blue analysis of nasal mucosa discolouration in allergic rhinitis
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 134 / Issue 4 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2020, pp. 332-337
- Print publication:
- April 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of two types of energy restriction on methylation levels of adiponectin receptor 1 and leptin receptor overlapping transcript in a mouse mammary tumour virus-transforming growth factor-α breast cancer mouse model
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 125 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2019, pp. 1-9
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Simultaneous skin friction and velocity measurements in high Reynolds number pipe and boundary layer flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 871 / 25 July 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2019, pp. 377-400
-
- Article
- Export citation
A comparative study of the velocity and vorticity structure in pipes and boundary layers at friction Reynolds numbers up to
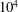 $10^{4}$
$10^{4}$
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 869 / 25 June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2019, pp. 182-213
-
- Article
- Export citation
Investigation of smell and taste function in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 133 / Issue 5 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2019, pp. 376-379
- Print publication:
- May 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Submandibular gland invasion and feasibility of gland-sparing neck dissection in oral cavity carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 132 / Issue 5 / May 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2018, pp. 446-451
- Print publication:
- May 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Classification of vertebral artery loop formation and association with cervicogenic dizziness
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 130 / Issue 12 / December 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2016, pp. 1115-1119
- Print publication:
- December 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
The role of the uncinate process in sinusitis aetiology: isolated agenesis versus maxillary sinus hypoplasia
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 129 / Issue 5 / May 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 April 2015, pp. 458-461
- Print publication:
- May 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mitral regurgitation: many reasons, multiple myocardial conditions, and several surgical options
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 25 / Issue 6 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2015, pp. 1230-1231
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Intellectual Property at the Edge
- Published online:
- 05 May 2014
- Print publication:
- 19 June 2014, pp x-xvi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Patterns of cervical lymph node metastases in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: implications for elective and therapeutic neck dissection
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 128 / Issue 3 / March 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2014, pp. 268-273
- Print publication:
- March 2014
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation of inferior turbinate hypertrophy in patients with congenital and traumatic nasal septum deviation
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 126 / Issue 8 / August 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2012, pp. 784-788
- Print publication:
- August 2012
-
- Article
- Export citation