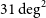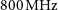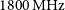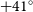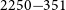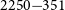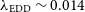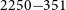74 results
RG-CAT: Detection pipeline and catalogue of radio galaxies in the EMU pilot survey
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, e027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Are Odd Radio Circles phoenixes of powerful radio galaxies?
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, e024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydrophobic Nature of Organo-Clays as a Lewis Acid/Base Phenomenon
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 327-334
-
- Article
- Export citation
Healthy Aging: Insights for Research and Policy
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 16 / Issue S1 / Spring Printemps 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 42-52
-
- Article
- Export citation
Measuring photometric redshifts for high-redshift radio source surveys
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, e039
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe Pilot Survey – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2022, e055
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe pilot survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2021, e046
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Australian square kilometre array pathfinder: I. system description
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preparation burning may not improve short-term seed survival in an Amazonian savanna
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 2 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2021, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey I: Design and first results
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2020, e048
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Great Dimming of Betelgeuse from the VLT/VLTI
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 16 / Issue S366 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2022, pp. 117-123
- Print publication:
- November 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PKS 2250–351: A giant radio galaxy in Abell 3936
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2020, e013
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Science with the Murchison Widefield Array: Phase I results and Phase II opportunities – Corrigendum
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, e014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Science with the Murchison Widefield Array: Phase I results and Phase II opportunities
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2019, e050
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Caesar source finder: Recent developments and testing
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 September 2019, e037
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
ASKAP commissioning observations of the GAMA 23 field
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2019, e024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The surface energies of cation substituted Laponite
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 28 / Issue 1 / March 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 July 2018, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bentonite reactivity in alkaline solutions: interim results of the Cyprus Natural Analogue Project (CNAP)
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 48 / Issue 2 / May 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 July 2018, pp. 235-249
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder: Performance of the Boolardy Engineering Test Array
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 33 / 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2016, e042
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Parkes-Tidbinbilla Interferometer
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 6 / Issue 2 / 1985
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2016, pp. 137-140
-
- Article
- Export citation