38 results
Impact of implementing a free varicella vaccination policy on incidence in Wuxi City, China: an interrupted time series analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2023, e125
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factual and counterfactual learning in major adolescent depressive disorder, evidence from an instrumental learning study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2023, pp. 256-266
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bubble production by air filament and cavity breakup in plunging breaking wave crests
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 929 / 25 December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2021, A44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Resistance switching behaviors of continuous-thick hBN films fabricated by radio-frequency-sputtering
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 23-24 / 14 December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2020, pp. 3247-3256
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Predictive indicators of severe COVID-19 independent of comorbidities and advanced age: a nested case−control study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2020, e255
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Permian to Late Triassic tectonics of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: geochronological and geochemical constraints from gabbros and granites in the northern Alxa area, NW China
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 157 / Issue 12 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2020, pp. 2089-2105
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Paradox of Academic Freedom in the Chinese Context
-
- Journal:
- History of Education Quarterly / Volume 58 / Issue 3 / August 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2018, pp. 447-452
- Print publication:
- August 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Geochronological and geochemical studies of the OIB-type Baiyanghe dolerites: implications for the existence of a mantle plume in northern West Junggar (NW China)
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 156 / Issue 4 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2018, pp. 702-724
-
- Article
- Export citation
Surface topography around the summit of Dome A, Antarctica, from real-time kinematic GPS
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 53 / Issue 180 / 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2017, pp. 159-160
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Current stage of the ATCA follow-up for SPLASH
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 13 / Issue S336 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2018, pp. 295-296
- Print publication:
- September 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Maternal iron intake during pregnancy and birth outcomes: a cross-sectional study in Northwest China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 117 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 April 2017, pp. 862-871
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nucleation of fractal nanocrystallites upon annealing of Fe-based metallic glass
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 32 / Issue 10 / 26 May 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2017, pp. 1880-1887
- Print publication:
- 26 May 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary intakes and dietary patterns among pregnant women in Northwest China
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / February 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2016, pp. 282-293
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ground-state OH maser distributions in the Galactic Centre region
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 11 / Issue S322 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2017, pp. 141-142
- Print publication:
- July 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Role played by the SP4 gene in schizophrenia and major depressive disorder in the Han Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 208 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2018, pp. 441-445
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Role of interface tailoring by Cu coating carbon nanotubes to optimize Cu–W composites
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 30 / Issue 24 / 28 December 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2015, pp. 3757-3765
- Print publication:
- 28 December 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
A novel method for determining surface residual stress components and their directions in spherical indentation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 30 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2015, pp. 1078-1089
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dense Plasma Torus in the GPS Galaxy NGC 1052
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 20 / Issue 1 / 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2013, pp. 134-139
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Free–Free Absorption and the Unified Scheme
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 20 / Issue 1 / 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2013, pp. 213-221
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Direct numerical simulation of a spatially developing compressible plane mixing layer: flow structures and mean flow properties
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 711 / 25 November 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2012, pp. 437-468
-
- Article
- Export citation

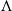 -vortices and hairpin vortices, breakdown of large structures and establishment of self-similar turbulence, is presented clearly in the simulation. In the transition process, the flow fields are populated sequentially by
-vortices and hairpin vortices, breakdown of large structures and establishment of self-similar turbulence, is presented clearly in the simulation. In the transition process, the flow fields are populated sequentially by 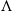 -vortices, hairpin vortices and ‘flower’ structures. This is the first direct evidence showing the dominance of these structures in the spatially developing mixing layer. Hairpin vortices are found to play an important role in the breakdown of the flow. The legs of hairpin vortices first evolve into sheaths with intense vorticity then break up into small slender vortices. The later flower structures are produced by the instability of the heads of the hairpin vortices. They prevail for a long distance in the mixing layer until the flow starts to settle down into its self-similar state. The preponderance of slender inclined streamwise vortices is observed in the transversal middle zone of the transition region after the breakup of the hairpin legs. This predominance of streamwise vortices also persists in the self-similar turbulent region, though the vortices there are found to be relatively very weak. The evolution of both the mean streamwise velocity profile and the Reynolds stresses is found to have close connection to the behaviour of the large vortex structures. High growth rates of the momentum and vorticity thicknesses are observed in the transition region of the flow. The growth rates in the self-similar turbulence region decay to a value that agrees well with previous experimental and numerical studies. Shocklets occur in the simulation, and their formation mechanisms are elaborated and categorized. This is the first three-dimensional simulation that captures shocklets at this low convective Mach number.
-vortices, hairpin vortices and ‘flower’ structures. This is the first direct evidence showing the dominance of these structures in the spatially developing mixing layer. Hairpin vortices are found to play an important role in the breakdown of the flow. The legs of hairpin vortices first evolve into sheaths with intense vorticity then break up into small slender vortices. The later flower structures are produced by the instability of the heads of the hairpin vortices. They prevail for a long distance in the mixing layer until the flow starts to settle down into its self-similar state. The preponderance of slender inclined streamwise vortices is observed in the transversal middle zone of the transition region after the breakup of the hairpin legs. This predominance of streamwise vortices also persists in the self-similar turbulent region, though the vortices there are found to be relatively very weak. The evolution of both the mean streamwise velocity profile and the Reynolds stresses is found to have close connection to the behaviour of the large vortex structures. High growth rates of the momentum and vorticity thicknesses are observed in the transition region of the flow. The growth rates in the self-similar turbulence region decay to a value that agrees well with previous experimental and numerical studies. Shocklets occur in the simulation, and their formation mechanisms are elaborated and categorized. This is the first three-dimensional simulation that captures shocklets at this low convective Mach number.