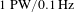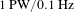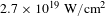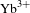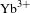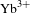71 results
Upregulation of miR-21-5p rescues the inhibition of cardiomyocyte proliferation induced by high glucose through negative regulation of Rhob
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 670-677
-
- Article
- Export citation
Zoonotic pathogens identified in rodents and shrews from four provinces, China, 2015–2022
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, e174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Seed biology of alkali barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli var. zelayensis) and junglerice (Echinochloa colona) for improved management in direct-seeded rice
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2023, pp. 112-123
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Straightforward Method for Measuring the Elastic and Inelastic Mean Free Paths for Scattering of Fast Electrons in Technologically Important Thin-Film Oxides
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 774-778
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Development and Evaluation of Innovative and Practical Table-top Exercises Based on a Real Mass-Casualty Incident
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, e200
-
- Article
- Export citation
Protective effect of antioxidants on cardiac function in adult offspring exposed to prenatal overnutrition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 13 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2022, pp. 741-749
-
- Article
- Export citation
CYP4CJ6-mediated resistance to two neonicotinoid insecticides in Sitobion miscanthi (Takahashi)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2022, pp. 646-655
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mapping non-laminar proton acceleration in laser-driven target normal sheath field
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2021, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Geochemistry of upper Palaeozoic ‘thin-layer’ limestones in the southern North China Craton: implications for closure of the northeastern Palaeotethys Ocean
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 4 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2021, pp. 494-510
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stabilization of the fluidic pinball with gradient-enriched machine learning control
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 917 / 25 June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2021, A42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modelling the potential non-breeding distribution of Spoon-billed Sandpiper Calidris pygmaea
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 31 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2020, pp. 169-184
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preparation, microstructure, and microhardness of selective laser-melted W–3Ta sample
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 15 / 14 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 2016-2024
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
The
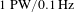 $1~\text{PW}/0.1~\text{Hz}$ laser beamline in SULF facility
$1~\text{PW}/0.1~\text{Hz}$ laser beamline in SULF facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 8 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2020, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The association between dietary protein intake, energy intake and physical frailty: results from the Rotterdam Study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 121 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2019, pp. 393-401
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Meta-analysis across Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology (CHARGE) consortium provides evidence for an association of serum vitamin D with pulmonary function
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 120 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2018, pp. 1159-1170
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Development and prospect of high-power
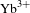 $\text{Yb}^{3+}$ doped fibers
$\text{Yb}^{3+}$ doped fibers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 6 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2018, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Studies of the relationship between rice stem composition and lodging resistance
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 156 / Issue 3 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2018, pp. 387-395
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The intertidal wetlands of southern Jiangsu Province, China – globally important for Spoon-billed Sandpipers and other threatened waterbirds, but facing multiple serious threats
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 27 / Issue 3 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2017, pp. 305-322
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation