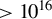157 results
301 W narrow-linewidth in-band pumped Er:Yb co-doped fiber amplifier at 1585 nm and related modeling for dynamics study and optimization
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, pp. 1-29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Workshop for the protection of Chinese giant salamanders
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The expansion and remaining suitable areas of global oil palm plantations
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 7 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An Axial Foilless Diode Guided by Composite Magnetic Field for the Production of Relativistic Electron Beams
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary inclusion of Clostridium butyricum cultures alleviated impacts of high-carbohydrate diets in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides)
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1308-1325
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Creative destruction, human capital accumulation, and growth in a digital economy
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanosecond laser conditioning of multilayer dielectric gratings for picosecond–petawatt laser systems
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, e89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Geothermal heat flow from borehole measurements at the margin of Princess Elizabeth Land (East Antarctic Ice Sheet)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 69 / Issue 277 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2023, pp. 1524-1528
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Autistic children’s visual sensitivity to face movement
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2023, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Linked patterns of symptoms and cognition with brain controllability in major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S420
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Using nomogram scores to predict the early regression of coronary artery aneurysms of Kawasaki disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2023, pp. 348-355
-
- Article
- Export citation
Analysis of the effect of psychological training on the treatment of the pre-competition psychological obstacles of ski jumpers
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2023, pp. S32-S33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Mid-Pleistocene drainage rearrangement of the Dadu River in response to plate convergence in southeastern Tibet
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 114 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2023, pp. 130-147
-
- Article
- Export citation
Patterns of brain dynamic functional connectivity are linked with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder-related behavioral and cognitive dimensions
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2023, pp. 6666-6677
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Longitudinal relations among family dysfunction, depressive symptoms, and cyberbullying involvement in Chinese early adolescents: Disentangling between- and within-person associations
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2022, pp. 395-403
-
- Article
- Export citation
Overview of the Maser Monitoring Organisation
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 18 / Issue S380 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2024, pp. 443-451
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation