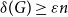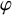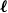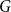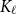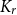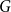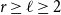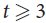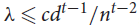67 results
Effects of Reaction Conditions on the Formation of Todorokite at Atmospheric Pressure
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 54 / Issue 5 / October 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 605-615
-
- Article
- Export citation
Manipulating the Laser-Driven Proton Bunch with Plasma Wakefield
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Professional Attitudes of Medical Students: A Pre-Post-Like Study
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, e555
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spanning trees in graphs without large bipartite holes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2023, pp. 270-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rainbow spanning structures in graph and hypergraph systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, e95
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Extremely powerful and frequency-tunable terahertz pulses from a table-top laser–plasma wiggler
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2023, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clique-factors in graphs with sublinear
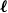 $\boldsymbol\ell$
-independence number
$\boldsymbol\ell$
-independence number
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 665-681
-
- Article
- Export citation
A study of the transmission characteristics of terahertz waves in hypersonic target flow field
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 88 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, 905880406
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Integrating morphological and contextual cues in lexical inferencing of Chinese fourth graders
-
- Journal:
- Applied Psycholinguistics / Volume 43 / Issue 4 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 805-827
-
- Article
- Export citation
Metabolic Score for Visceral Fat: a novel predictor for the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2021, pp. 1029-1036
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clinical Characteristics and Abnormal Parameters Evolution in Patients With Novel Coronavirus Infection: A Case Series of 272 Cases in Guangzhou
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2021, pp. 2492-2498
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Low selenium intake is associated with postpartum weight retention in Chinese women and impaired physical development of their offspring
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2021, pp. 1498-1509
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Near-perfect clique-factors in sparse pseudorandom graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2020, pp. 570-590
-
- Article
- Export citation
Petrogenesis of Silurian ultramafic–mafic plutons in southern Jiangxi: implications for the Wuyi–Yunkai orogen, South China
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 158 / Issue 7 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2020, pp. 1237-1252
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mental health services for infectious disease outbreaks including COVID-19: a rapid systematic review
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 15 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, pp. 2498-2513
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Covering and tiling hypergraphs with tight cycles
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 2 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2020, pp. 288-329
-
- Article
- Export citation
A new tetraradial olivooid (Medusozoa) from the lower Cambrian (Stage 2) Yanjiahe Formation, South China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 94 / Issue 3 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2019, pp. 457-466
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shotgun metagenomics reveals both taxonomic and tryptophan pathway differences of gut microbiota in major depressive disorder patients
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2019, pp. 90-101
-
- Article
- Export citation