36 results
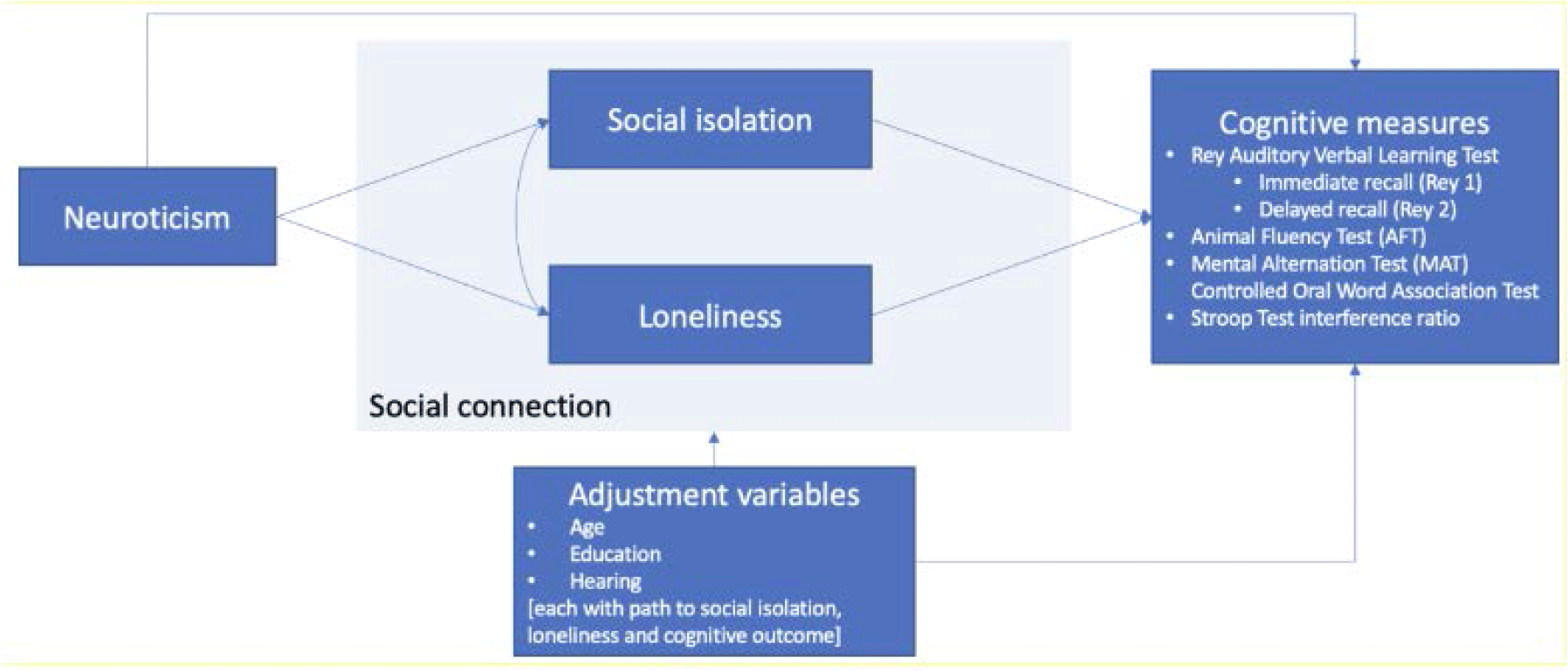
FC30: The relationships between neuroticism, social connection and cognition
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 92-94
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
54 The Differential Impact of Genetic Moderators on the Relationship Between Depression and Cognition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 659-660
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
4 Methamphetamine, cannabis, HIV, and their combined effects on neurocognition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 797-798
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Cannabis use may attenuate neurocognitive performance deficits resulting from methamphetamine use disorder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. 84-93
-
- Article
- Export citation
Serving decision makers and their employees simultaneously: Adopting a balanced approach
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 16 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2023, pp. 113-116
-
- Article
- Export citation
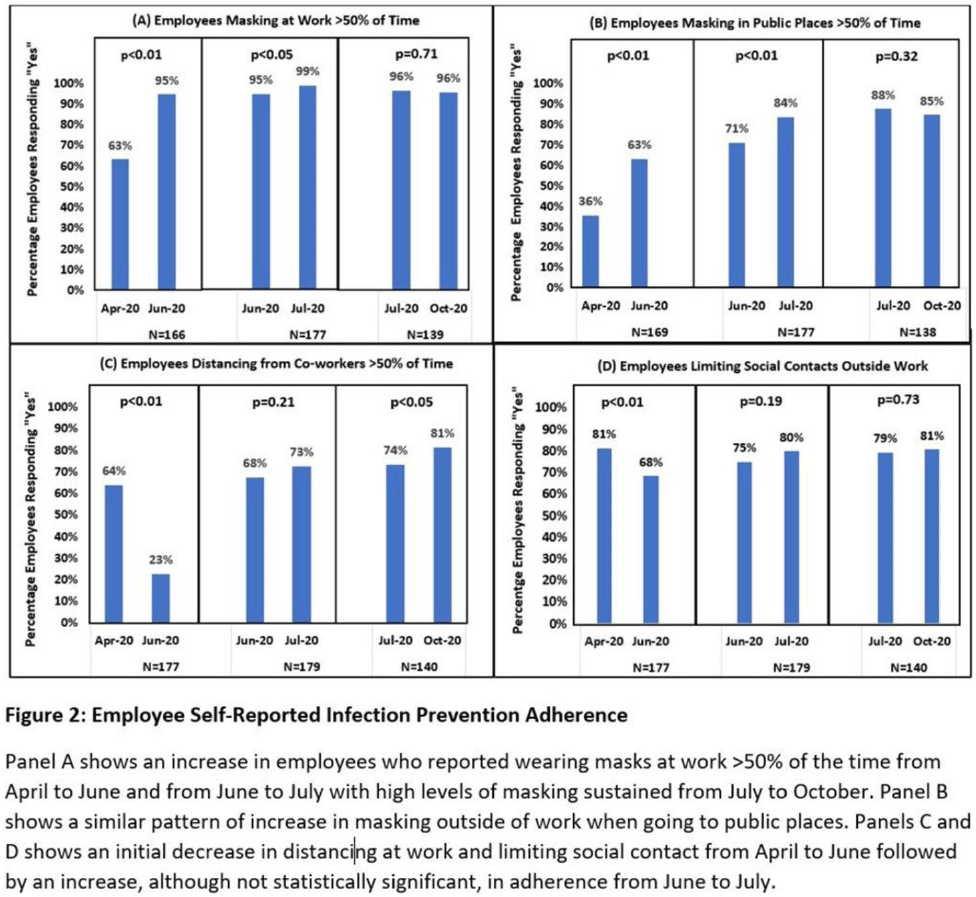
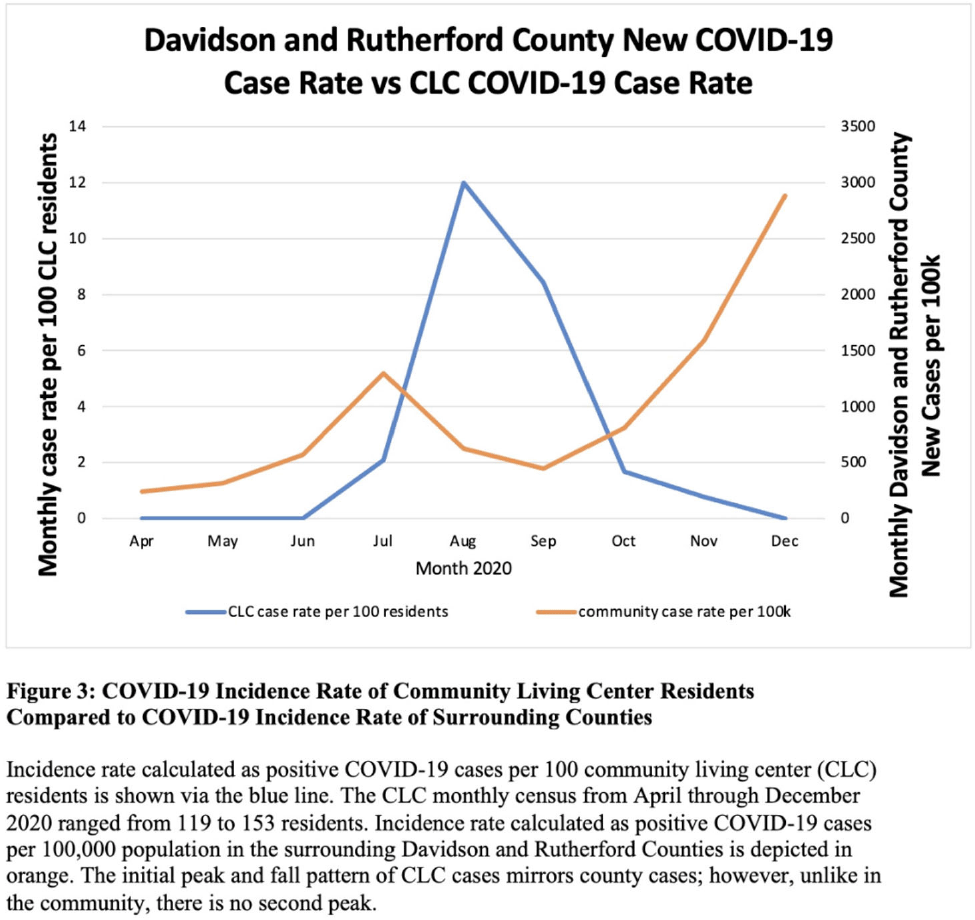
Long-term care facility employee infection prevention adherence and prevention of COVID-19 outbreaks in a high-incidence area
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, pp. s50-s51
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Risk of bacterial bloodstream infection does not vary by central-line type during neutropenic periods in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2022, pp. 222-229
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Healthcare design to improve safe doffing of personal protective equipment for care of patients with COVID-19
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 12 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2022, pp. 1796-1805
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Opportunities to address the failure of online food retailers to ensure access to required food labelling information in the USA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2022, pp. 1375-1383
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
12 - The Power of Civil Society
-
-
- Book:
- Negotiating the Paris Agreement
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 245-264
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Daily Cannabis Use is Associated With Lower CNS Inflammation in People With HIV
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 27 / Issue 6 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2021, pp. 661-672
-
- Article
- Export citation
Development of an international template to support patient submissions in Health Technology Assessments
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2021, e50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morphometrics of 39 fishes from the Seychelles artisanal fisheries
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 100 / Issue 8 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2021, pp. 1327-1336
-
- Article
- Export citation
Recreating the OSIRIS-REx slingshot manoeuvre from a network of ground-based sensors
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 November 2020, e049
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Understanding Aging, Frailty, and Resilience in Ontario First Nations
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2020, pp. 512-517
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characteristics of Young-Onset and Late-Onset Dementia Patients at a Remote Memory Clinic
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 47 / Issue 3 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2020, pp. 320-327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Current infection prevention and antibiotic stewardship program practices: A survey of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) Research Network (SRN)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 40 / Issue 9 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2019, pp. 1046-1049
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hospital epidemiologists’ and infection preventionists’ opinions regarding hospital-onset bacteremia and fungemia as a potential healthcare-associated infection metric
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 40 / Issue 5 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2019, pp. 536-540
- Print publication:
- May 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Can a shift in the purchase of local foods by Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) recipients impact the local economy?
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems / Volume 35 / Issue 1 / February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2018, pp. 90-101
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chandra Early-Type Galaxy Atlas
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 14 / Issue S342 / May 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 April 2020, pp. 242-243
- Print publication:
- May 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation