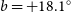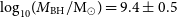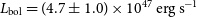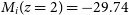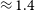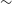352 results
Alleviating the burden of depression: a simulation study on the impact of mental health services
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of measurement and feedback on chlorhexidine gluconate bathing among intensive care unit patients: A multicenter study
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 1375-1380
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Agricultural Research Service Weed Science Research: Past, Present, and Future
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2023, pp. 312-327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
22 - The Wolves of Yellowstone: Saviours of the Songbird or Pieces of the Puzzle?
-
-
- Book:
- The Wolf
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 10 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 18 July 2023, pp 249-258
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and associated risk factors among staff and residents at homeless shelters in King County, Washington: an active surveillance study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2023, e129
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of U.S. Army Soldiers wearing a back exosuit during a field training exercise
-
- Journal:
- Wearable Technologies / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 July 2023, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modeling the potential distribution of the threatened Grey-necked Picathartes Picathartes oreas across its entire range
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 33 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2023, e65
-
- Article
- Export citation
325 Predictors of Substance Use Initiation by Late Childhood: Findings from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, p. 97
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Slower self-reported eating rate is associated with favourable cardio-metabolic risk factors in UK adults
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2023, E32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Successful Mother- and Group-Rearing of a Newborn Capuchin Monkey (Cebus Capucinus) Following Emergency Major Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 4 / Issue 3 / August 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 171-182
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vitamin a Metabolism in Recessive White Canaries
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 9 / Issue 2 / May 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 153-165
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plasma image classification using cosine similarity constrained convolutional neural network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 88 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2022, 895880603
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Development and application of novel performance validity metrics for computerized neurocognitive batteries
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue 8 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, pp. 789-797
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Influences on the development of imaginary worlds
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 45 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2022, e307
-
- Article
- Export citation
Discovery of the most luminous quasar of the last 9 Gyr
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2022, e037
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Alcohol use disorder as a risk factor for violent offending in a sample of female forensic-psychiatric inpatients
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S348
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The incidence of Orientia tsutsugamushi infection in rural South India
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2022, e132
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiology and genomics of a slow outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphyloccus aureus (MRSA) in a neonatal intensive care unit: Successful chronic decolonization of MRSA-positive healthcare personnel
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 June 2022, pp. 589-596
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Computer Aided Ergonomics: Evaluation Study of a Interaction Model for Digital Human Models
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2022, pp. 663-672
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Time to death and risk factors associated with mortality among COVID-19 cases in countries within the WHO African region in the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 February 2022, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation