159 results
54 Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia with Lewy Bodies
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 260-261
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Biocultural aspects of species extinctions
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Extinction / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2023, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
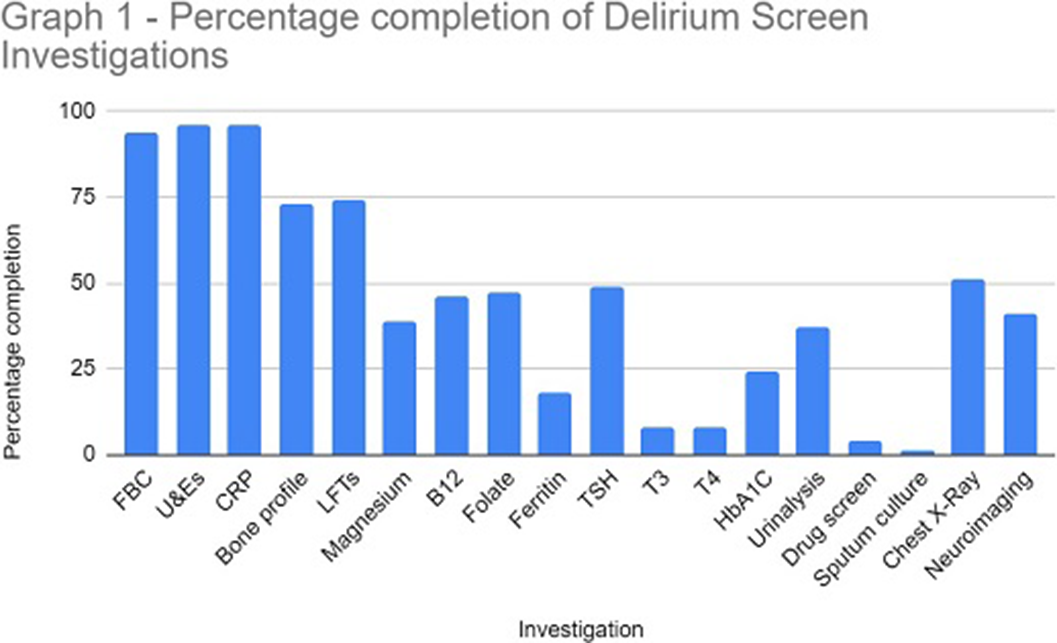
Are We Adequately Assessing Delirium? An Analysis Of Liaison Psychiatry Referrals
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S518-S519
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Life stress and Bipolar Disorder: regarding a clinical case
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S712
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Cerebellar dysfunction and autism spectrum disorders – what do we know?
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S239
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Prevalence of Traumatic Brain Injury and ADHD in Secure Settings
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue S1 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 July 2023, pp. S8-S9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A review of succession strategies in family business: content analysis and future research directions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2022, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sex differences in total brain volume in a cognitively unimpaired elderly population
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, p. S407
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Protective effects of whey protein concentrate admixtured of curcumin on metabolic control, inflammation and oxidative stress in Wistar rats submitted to exhaustive exercise
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2021, pp. 526-539
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The cost of metastatic prostate cancer using time-driven activity-based costing
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2021, e60
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli (DEC) and Salmonella spp. with zoonotic potential in urban rats in Salvador, Brazil
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2020, e128
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The role of coherent structures and inhomogeneity in near-field interscale turbulent energy transfers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 896 / 10 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2020, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
P01-08 - Mania, Mania with Delirium and Delirious Mania
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 25 / Issue S1 / 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2020, 25-E213
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
FC12.04 May P300 help differentiate the syndromatic patterns in schizophrenia?
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 15 / Issue S2 / October 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 306s
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Preliminary Data from Famidem Survey: Can we assume who is at Risk Regarding Informal Caregiving in Dementia?
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 24 / Issue S1 / January 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, 24-E1100
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Autoantibodies in Bipolar and Cluster B Personality Disorders
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 24 / Issue S1 / January 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, 24-E547
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
is Feigned Psychosis a Pathway to Schizophrenia?
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 24 / Issue S1 / January 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, 24-E1111
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
EPA-0485 - Evaluating the Somatic Impairments in the Elderly: Preliminary Results of the 10/66-Dementia Research Group Prevalence Study in Portugal
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 29 / Issue S1 / 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation