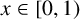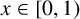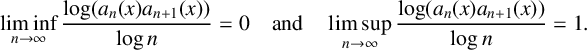1924 results
Clay and Fe (oxyhydr)oxide mineralogy in the basalt weathering profile in Hainan (southern China): implications for pedogenesis process
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 72 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2024, e8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Diagnosing the fast-heating process of the double-cone ignition scheme with x-ray spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
“You act as Human, and I will act as AI”: Technological Rehearsals at the Interface
-
- Journal:
- TDR: The Drama Review / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 131-150
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Translating impartiality into operations from a financial perspective: Uncertainties and solutions
-
- Journal:
- International Review of the Red Cross , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, pp. 1-37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modelling the first droplet emission from an electrified liquid meniscus hanging at the nozzle tip
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, A38
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mortality risk and mood stabilizers in bipolar disorder: a propensity-score-weighted population-based cohort study in 2002–2018
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multidimensional Analysis of PANoptosis-Related Molecule CASP8: Prognostic Significance, Immune Microenvironment Effect, and Therapeutic Implications in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2024, e38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Does checking-in help? Understanding L2 learners’ autonomous check-in behavior in an English-language MOOC through learning analytics
-
- Journal:
- ReCALL , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vortex-induced rotation of a square cylinder under the influence of Reynolds number and density ratio
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 986 / 10 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2024, A15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Random analytic functions with a prescribed growth rate in the unit disk
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2024, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
- Export citation
ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR FOR PRODUCTS OF CONSECUTIVE PARTIAL QUOTIENTS IN CONTINUED FRACTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of retrieval schedules on the acquisition of explicit, automatized-explicit, and implicit knowledge of L2 collocations
-
- Journal:
- Studies in Second Language Acquisition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mood disorders influencing endometriosis and adenomyosis: Mendelian randomisation study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, e83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the low-frequency flapping motion in flow separation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, A76
-
- Article
- Export citation
Psychosocial and psychological interventions for schizophrenia relapse prevention: A bibliometric analysis
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 11 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Longitudinal association between soft drink consumption and handgrip strength in adults: a prospective analysis from the Tianjin Chronic Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation and Health (TCLSIH) cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1997-2004
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Decreased risk of non-influenza respiratory infection after influenza B virus infection in children
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, e60
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relationship between syncopal symptoms and head-up tilt test modes
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
44 Trends in Management of Chronic Kidney Disease among Adults with Diabetes, NHANES 1988-2020
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, pp. 11-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
303 Social Network Analysis of Patient Sharing Among Providers: Implications for Analyzing Disparities in Cancer Screening
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation