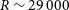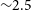224 results
P63: Best Practice Guidance on Human Interaction with Technology in Dementia Update June 2023 – Recommendations from the INDUCT and DISTINCT Networks
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 158-159
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Optimising motor development in the hospitalised infant with CHD: factors contributing to early motor challenges and recommendations for assessment and intervention
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2023, pp. 1800-1812
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Agricultural Research Service Weed Science Research: Past, Present, and Future
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2023, pp. 312-327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and associated risk factors among staff and residents at homeless shelters in King County, Washington: an active surveillance study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2023, e129
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of U.S. Army Soldiers wearing a back exosuit during a field training exercise
-
- Journal:
- Wearable Technologies / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 July 2023, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modeling the potential distribution of the threatened Grey-necked Picathartes Picathartes oreas across its entire range
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 33 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2023, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relationship between the response to the corneal reflex (depth of narcosis) and specific parameters in the slaughter blood of pigs narcotised with CO2
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 19 / Issue 4 / November 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 515-522
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Development and application of novel performance validity metrics for computerized neurocognitive batteries
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue 8 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, pp. 789-797
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Archaeology and Social Justice in Native America – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 87 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2022, p. 864
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Archaeology and Social Justice in Native America
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 87 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2022, pp. 659-682
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiology and genomics of a slow outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphyloccus aureus (MRSA) in a neonatal intensive care unit: Successful chronic decolonization of MRSA-positive healthcare personnel
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 June 2022, pp. 589-596
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Holocene water levels of Silver Lake, Montana, and the hydroclimate history of the Inland Northwest
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 110 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 54-66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The formation of planetary systems with SPICA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2021, e055
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A laboratory method for mass rearing the orange wheat blossom midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae)
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 153 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2021, pp. 828-836
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anatomy of a successful stewardship intervention: Improving perioperative prescribing in penicillin-allergic patients
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 9 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2021, pp. 1101-1107
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design, installation and commissioning of the ELI-Beamlines high-power, high-repetition rate HAPLS laser beam transport system to P3
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2021, e30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
What is quantitative plant biology?
-
- Journal:
- Quantitative Plant Biology / Volume 2 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2021, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Variable selection methods for identifying predictor interactions in data with repeatedly measured binary outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 5 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2020, e59
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory: A kilohertz-band gravitational-wave detector in the global network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The origin and impact of Wolf-Rayet-type mass loss
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 16 / Issue S366 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2022, pp. 21-26
- Print publication:
- November 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation