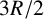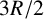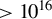678 results
Impact of the Covid pandemic on the mental health of children and young people with pre-existing mental health and neurodevelopmental conditions: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, p. S138
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Analysis and forecasting of syphilis trends in mainland China based on hybrid time series models
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2024, e93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Development and validation of a nonverbal consensus-based semantic memory paradigm in patients with epilepsy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A molecular perspective on the genera Paragonimus Braun, Euparagonimus Chen and Pagumogonimus Chen
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 73 / Issue 4 / April 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 295-299
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adverse childhood experiences and unhealthy dietary behaviours in adulthood
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Validation of microRNAs regulated by vitamin D and lipid loading in immortalised hepatocytes
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E354
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thiourea-Induced Change of Structure and Color of Brick-Red Palygorskite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 5 / October 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 403-414
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanoscale Elastic Properties of Dry and wet Smectite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 209-219
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fabrication of Anthocyanin/Montmorillonite Hybrid Pigments to Enhance Their Environmental Stability and Application in Allochroic Composite Films
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 142-151
-
- Article
- Export citation
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF APPARATUS-INDUCED DISPERSION FOR DENSITY-DEPENDENT SOLUTE TRANSPORT IN POROUS MEDIA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 1-2 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 178-194
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Psychological effects of PTSD and major depression following the wildfires in Fort McMurray: A fifth-year post-disaster study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S472
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Fort McMurray: Prevalence and Correlates One Year After the Flood
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S477
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Assessing enrollment of eligible infants in the national pediatric cardiology quality improvement collaborative (NPC-QIC) through linkage to the pediatric cardiac critical care consortium (PC4) registry
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2023, pp. 373-379
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early life adversity predicts an accelerated cellular aging phenotype through early timing of puberty
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 16 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 June 2023, pp. 7720-7728
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental investigation on droplet evaporation characteristics during combustion of future and current aviation fuels with range of properties
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1317 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2023, pp. 1952-1967
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fixed-time cooperative trajectory optimisation strategy for multiple hypersonic gliding vehicles based on neural network and ABC algorithm
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1316 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2023, pp. 1737-1751
-
- Article
- Export citation
446 To Stay or Not to Stay: Multidisciplinary Collaboration After NSF Funding
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 132-133
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Post-operative vestibular and equilibrium evaluation in patients with cholesteatoma-induced labyrinthine fistulas
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, pp. 16-21
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation