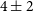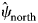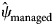162 results
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey III: Spectra and Polarisation In Cutouts of Extragalactic Sources (SPICE-RACS) first data release – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, e039
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The role of psychosis and clozapine load in excessive checking in treatment-resistant schizophrenia: longitudinal observational study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 224 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2024, pp. 164-169
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dehydration, Diffusion and Entrapment of Zinc in Bentonite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / April 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 132-138
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acceptability of self-administered antigen test for COVID-19 in the Philippines
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lim Ulrich sequences and Boij-Söderberg cones
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, e115
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey III: Spectra and Polarisation In Cutouts of Extragalactic Sources (SPICE-RACS) first data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2023, e040
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparing the distribution of neuropsychiatric symptoms among individuals with depression and mild cognitive impairment
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S173
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
GR.2 A deep intronic FGF14 GAA repeat expansion causes late-onset cerebellar ataxia
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Raccoon rabies control and elimination in the northeastern USA and southern Québec, Canada
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, e62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Depolarization of intense laser beams by dynamic plasma density gratings
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2023, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A systematic study on 33 gallbladder stones resembling adult Clonorchis sinensis worms
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 96 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2022, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Teachers’ perceived corpus literacy and their intention to integrate corpora into classroom teaching: A survey study
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The TIMEBASE Study: IdenTifying dIgital bioMarkers of illnEss activity in BipolAr diSordEr. Preliminary results
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S221
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
P.015 Monthly migraine days, acute medication use-days, and migraine-specific quality of life in responders to atogepant: a post hoc analysis
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue s1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, p. S11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
GASKAP-HI pilot survey science I: ASKAP zoom observations of Hi emission in the Small Magellanic Cloud
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (vitamin D) level among children with ventricular septal defect: how big is the risk for pulmonary hypertension?
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 12 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2022, pp. 1984-1988
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spatial epidemiological characteristics and exponential smoothing model application of tuberculosis in Qinghai Plateau, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2022, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neural effects of antidepressant medication and psychological treatments: a quantitative synthesis across three meta-analyses
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 4 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 February 2021, pp. 546-550
- Print publication:
- October 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effect of cereal type and α-tocopherol supplementation on selective quality and processability parameters of milk from late lactation grazing dairy cows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 88 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2021, pp. 29-32
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
The influence of prescriber and patient gender on the prescription of benzodiazepines: results from the Florida Medicaid Dataset
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 27 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2021, pp. 378-382
-
- Article
- Export citation