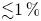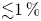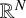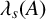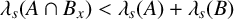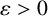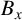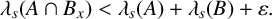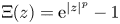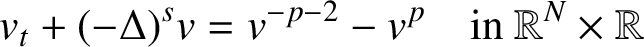87 results
Insights into the deployment of a social robot-augmented telepresence robot in an elder care clinic – perspectives from patients and therapists: a pilot study
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. 1-29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Predicting turbulent dynamics with the convolutional autoencoder echo state network
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2023, A2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incomplete to complete multiphysics forecasting: a hybrid approach for learning unknown phenomena
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SG-APSIC1064: The role of infection control activities on healthcare-associated infections during 2017-2021 at intensive care units in Cho Ray Hospital – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2023, e160
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A randomised controlled school-based nutritional intervention in five Middle Eastern countries: Ajyal Salima improved students’ dietary and physical activity habits
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2023, pp. 2036-2047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SG-APSIC1064: The role of infection control activities on healthcare-associated infections during 2017-2021 at intensive care units in Cho Ray Hospital
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, pp. s18-s19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
SG-APSIC1100: Healthcare-associated infections in COVID-19 patients in Vietnam: Are we able to respond better?
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, p. s18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
SG-APSIC1117: Healthcare-associated infections among the obstetrics and gynecology patients with confirmed COVID-19 in Hung Vuong Hospital, Vietnam
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, pp. s6-s7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
SG-APSIC1011: Factors associated with improved knowledge of COVID-19 prevention and control following a training of healthcare workers in Vietnam
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, pp. s10-s11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Community engagement strategies to promote recruitment and participation in clinical research among rural communities: A narrative review
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2023, e84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON THE LOWEST EIGENVALUE OF THE FRACTIONAL LAPLACIAN FOR THE INTERSECTION OF TWO DOMAINS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 108 / Issue 2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2022, pp. 290-297
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Successful Case of Cardiac Arrest due to Acute Myocarditis with COVID-19: 120 Minutes on Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation then Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 37 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2022, pp. 843-846
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Efficient Method of Observing Diatom Frustules via Digital Holographic Microscopy
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2022, pp. 2172-2176
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Interventions for mental health, cognition, and psychological wellbeing in long COVID: a systematic review of registered trials
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 13 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2022, pp. 2426-2440
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Status of a second viable population of the Critically Endangered Delacour's langur in Viet Nam
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chaotic systems learning with hybrid echo state network/proper orthogonal decomposition based model
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 2 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2021, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the initial value problem for a class of nonlinear biharmonic equation with time-fractional derivative
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2021, pp. 989-1031
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Forced Migration, Oceanic Humanitarianism, and the Paradox of Danger and Saviour of a Vietnamese Refugee Boat Journey
-
- Journal:
- The Historical Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2021, pp. 505-526
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
DO WEAK OR STRONG ACIDS REMOVE CARBONATE CONTAMINATION FROM ANCIENT TOOTH ENAMEL MORE EFFECTIVELY? THE EFFECT OF ACID PRETREATMENT ON RADIOCARBON AND δ13C ANALYSES
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 63 / Issue 3 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2021, pp. 935-952
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
UNIFORM LOWER BOUND AND LIOUVILLE TYPE THEOREM FOR FRACTIONAL LICHNEROWICZ EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 104 / Issue 3 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2021, pp. 484-492
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation