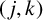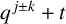10613 results

Understanding Visuals in the Life Sciences
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- September 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation

The Roman Republic and Political Culture
- German Scholarship in Translation
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- September 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Place and Performance in Ancient Greece, Rome, and China
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- August 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 August 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Mitochondrial protective potential of fucoxanthin in brain disorders
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 13 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2024, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Australian Banking and Finance Law and Regulation
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- July 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 July 2024
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
Chapter 19 - Critical and Literary Theory
- from Part III - Cultural Transfers
-
-
- Book:
- Europe in British Literature and Culture
- Print publication:
- 13 June 2024, pp 306-321
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

Ethics in Econometrics
- A Guide to Research Practice
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- June 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Two - Greek Iron Age Pottery in the Mediterranean World
-
-
- Book:
- Greek Iron Age Pottery in the Mediterranean World
- Published online:
- 30 May 2024
- Print publication:
- 06 June 2024, pp 14-50
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Disease Burden attributable to High Body Mass Index in Belt and Road Initiative Countries, 1990-2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2024, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Non-monotonic effect of compaction on longitudinal dispersion coefficient of porous media
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 988 / 10 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2024, R2
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Influence of Space Environmental Factors on the Laser-induced Damage Thresholds in Optical Components
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
CHARACTERISTIC POLYNOMIALS OF THE MATRICES WITH
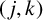 $(\,j,k)$-ENTRY
$(\,j,k)$-ENTRY 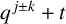 $q^{\,j\pm k}+t$
$q^{\,j\pm k}+t$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cost–utility analysis of Social Stories™ for children with autism spectrum disorder in mainstream primary schools: results from a randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, e123
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cross-sectional Relationship Between Dietary Protein Intake, Energy Intake and Protein Energy Wasting in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Evidence-Based Physiotherapeutic Interventions Enhancing Hand Dexterity, Activities of Daily Living and Quality of Life of Parkinson’s Disease Patients: A Systematic Review
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.100 Plasma extracellular vesicle sampling from high grade gliomas demonstrates a small RNA signature indicative of disease and identifies lncRNA RPPH1 as a novel biomarker
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Markwelchite, TlPbSbS3, a new Tl-Pb sulfosalt from the hydrothermal deposit of Jas Roux, Hautes-Alpes, France
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
E.2 Proof of concept for liquid biopsy: positive correlation between extracellular vesicles shed by high grade gliomas and volume of hypervascular tumour tissue on MRI
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.099 Transfer RNA fragments in patient plasma extracellular vesicles as biomarkers of high grade glioma
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.033 Electrophysiological signatures of sedation in pediatric patients
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation