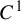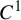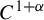26 results
Incidence of mental health diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multinational network study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Measures of maximal and full dimension for smooth maps
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2023, pp. 31-49
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interparental conflict and depressive symptoms among Chinese adolescents: A longitudinal moderated mediation model
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2022, pp. 972-981
-
- Article
- Export citation
Self-similarity in particle accumulation on the advancing meniscus
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 925 / 25 October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2021, A10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Histone Demethylase KDM4D Could Improve the Developmental Competence of Buffalo (Bubalus Bubalis) Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) Embryos
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2021, pp. 409-419
- Print publication:
- April 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary betaine intake is associated with skeletal muscle mass change over 3 years in middle-aged adults: the Guangzhou Nutrition and Health Study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 125 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 July 2020, pp. 440-447
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Slab break-off origin of 105 Ma A-type porphyritic granites in the Asa area of Tibet
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 157 / Issue 8 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2020, pp. 1281-1298
-
- Article
- Export citation
Parenting style, coping efficacy, and risk-taking behavior in Chinese young adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology / Volume 14 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2020, e3
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Serum folate concentrations at diagnosis are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma survival in the Guangdong Liver Cancer Cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 121 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 June 2019, pp. 1376-1388
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vacuum brazing of TC4 alloy to AlMgB14–TiB2 ceramic using AgCu filler
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 14 / 28 July 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2019, pp. 2535-2542
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
The delayed degradation mechanism and mechanical properties of β-TCP filler in poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/beta-tricalcium phosphate composite suture anchors during short-time degradation in vivo
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 33 / Issue 24 / 28 December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2018, pp. 4278-4286
- Print publication:
- 28 December 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
The computational power of timed P systems with active membranes using promoters
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Structures in Computer Science / Volume 29 / Issue 5 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2018, pp. 663-680
-
- Article
- Export citation
Serum CRP Concentrations and Severity of Ischemic Stroke Subtypes
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / January 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2014, pp. 69-73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Genetic-basis analysis of heterotic loci in Dongxiang common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.)
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 94 / Issue 2 / April 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2012, pp. 57-61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Construction and Prospects of the Chongqing Twin Children Database
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 11 / Issue 6 / 01 December 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2012, pp. 629-633
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Research progress in techniques for detecting genetically modified organisms
-
- Journal:
- Chinese Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / April 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2009, pp. 1-9
- Print publication:
- April 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation
Establishment of real-time fluorescent PCR assay to detect Streptococcus suis serotype 2
-
- Journal:
- Chinese Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology / Volume 4 / Issue 1 / April 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2007, pp. 69-74
- Print publication:
- April 2007
-
- Article
- Export citation
Real-time quantitative PCR detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7
-
- Journal:
- Chinese Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology / Volume 4 / Issue 1 / April 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2007, pp. 15-19
- Print publication:
- April 2007
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for PAT protein detection in genetically modified rape
-
- Journal:
- Chinese Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology / Volume 3 / Issue 3 / December 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2007, pp. 177-181
- Print publication:
- December 2006
-
- Article
- Export citation