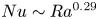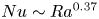250 results
Compression and acceleration processes of spherical shells in gold cones
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Deblending overlapping galaxies in DECaLS using transformer-based algorithm: A method combining multiple bands and data types
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, e035
-
- Article
- Export citation
Escaping the organization: Examining the influence of supervisor bottom-line mentality on employee withdrawal
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mineralogy of Dickite and Nacrite From Northern Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 49 / Issue 6 / December 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 586-595
-
- Article
- Export citation
Revealing complexity: Segmentation of hippocampal subfields in adolescents with major depressive disorder reveals specific links to cognitive dysfunctions
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
P203: The temporal relationship between dementia and serious traffic accidents: a cohort study of linked national databases.
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 189-190
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Reconstruction and analysis of the transmission network of African swine fever in People’s Republic of China, August 2018–September 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Patterns of polysomnography parameters in 27 neuropsychiatric diseases: An umbrella review – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, p. 435
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Kaolin Minerals from Chinmen Island (Quemoy)
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 130-137
-
- Article
- Export citation
Thermal Characterization of Surfactant-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 53 / Issue 3 / June 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 287-293
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Protective Effect of Trichosanthes kirilowii Peel Polysaccharide on the Oxidative Damaged HepG2 and HUASMC Cells
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Seasonal Variation in the Mineralogy of the Suspended Particulate Matter of the Lower Changjiang River at Nanjing, China
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 5 / October 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 691-706
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis of the Effect of β-Elemene on Colorectal Cancer from the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clinical and genetic characteristics of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia combined with left ventricular non-compaction
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Protective factors for children with autism spectrum disorder during COVID-19-related strict lockdowns: a Shanghai autism early developmental cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 6 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 1102-1112
-
- Article
- Export citation
Strong coupling of flow structure and heat transport in liquid metal thermal convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, A21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Taste preferences, cardiometabolic diseases and mild cognitive impairment: a prospective cohort analysis of older Chinese adults
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, pp. 1064-1073
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Changing trends in the global burden of mental disorders from 1990 to 2019 and predicted levels in 25 years
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The guiding effect of clothing design assisted therapy based on Chinese elements on young patients with autism
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. S139-S140
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation