8332 results

Web3
- Blockchain, the New Economy, and the Self-Sovereign Internet
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- November 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Key factors affecting overexpanded flow separation in design of large expansion ratio single expansion ramp nozzle
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of cardiometabolic multimorbidity with risk of late-life depression: a nationwide twin study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2024, e58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Shub’s example revisited
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2024, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Developmental human resource practices, thriving at work, and employee agility: The moderating role of workplace spirituality
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Endogenous innovation scale and patent policy in a monetary schumpeterian growth model
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
New SIMS U–Pb zircon age on the macroscopic multicellular eukaryotes from the early Mesoproterozoic Gaoyuzhuang Formation, North China
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2024, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Advancing digital healthcare engineering for aging ships and offshore structures: an in-depth review and feasibility analysis – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 5 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The embodiment of power as upward/downward movement in Chinese-English bilinguals
-
- Journal:
- Applied Psycholinguistics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Predicting potential habitat distribution of the invasive species Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Olivier in China based on MaxEnt modelling technique and future climate change
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effects of lead (Pb) and pest damage on soil enzyme activities, pakchoi and Spodoptera litura performance
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
RGB-D visual odometry by constructing and matching features at superpixel level
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Treatment-related Problems and Countermeasures for Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis Following Tropical Cyclones: A Scoping Review
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, e117
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Time Pattern of Presentation of Victims of High-Speed Passenger Ferry Mass Casualty Incidents to the Emergency Department
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, e123
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optimal avoidance strategy based on nonlinear approximate analytic solution of non-cooperative differential game
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Robust motion planning for mobile robots under attacks against obstacle localization
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
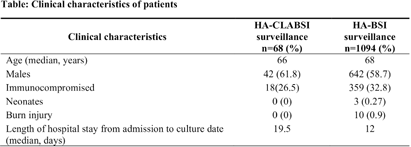
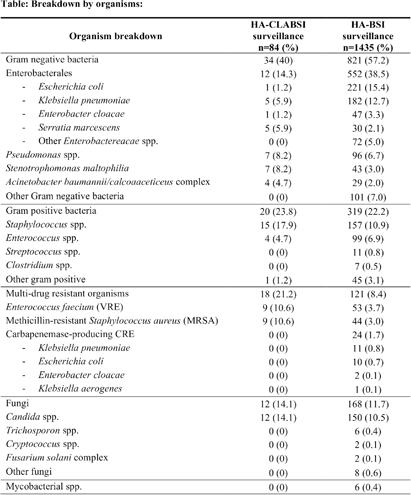
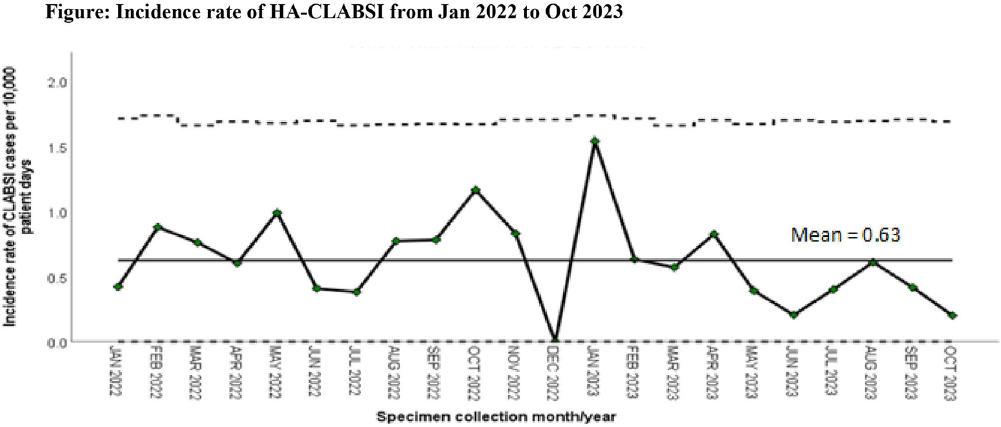
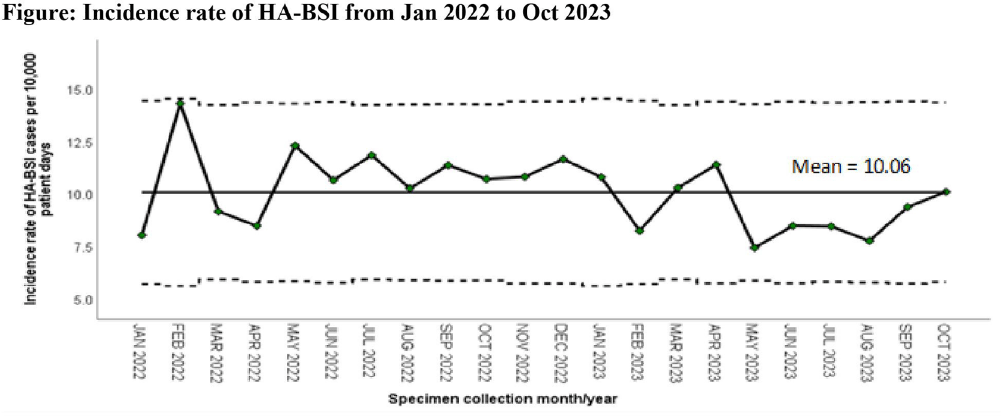
Comparative Analysis of Healthcare-associated Bloodstream Infections & CLABSI Surveillance in A Singaporean tertiary Hospital
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. s154-s155
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Mechanical properties of pressure-frozen ice under triaxial compressive stress
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Combining spatial clustering and tour planning for efficient full area exploration
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Double diffusive convection in the diffusive regime with a uniform background shear
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 993 / 25 August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2024, A14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation