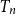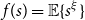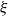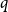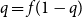363 results
Characterizing the distinct imaging phenotypes, clinical behavior, and genetic vulnerability of brain maturational subtypes in mood disorders
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 May 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A.6 INDIGO: a global, randomized, double-blinded, Phase 3 study of vorasidenib versus placebo in patients with grade 2 glioma with an IDH1/2 mutation (mIDH1/2)
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The effects of fermented vegetables on the gut microbiota for prevention of cardiovascular disease
-
- Journal:
- Gut Microbiome / Volume 5 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterisation of the mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic analysis of Toxocara apodemi (Nematoda: Ascarididae)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, e33
-
- Article
- Export citation
Validation of the Passive Surveillance Stroke Severity Score in Three Canadian Provinces
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ultrafast High-Energy Electron Radiography Application in Magnetic Field Delicate Structure Measurement
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Linked patterns of symptoms and cognition with brain controllability in major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S420
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Propeller control for takeoff of a heavily loaded coaxial compound helicopter
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1316 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, pp. 1832-1849
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of psychological treatment for depression among people not actively seeking help: a meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 320-331
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nonlinear harmonics of gap fluid resonance with floating body motions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 951 / 25 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2022, A23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A molecular dynamics study of the mechanical properties of kaolinite under uniaxial and isothermal compression at various temperatures
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2022, pp. 131-138
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal mental health during pregnancy: The CONCEPTION study – Phase I
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, pp. S209-S210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Steinernema populi n. sp. (Panagrolaimomorpha, Steinernematidae), a new entomopathogenic nematode species from China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 96 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2022, e57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Volume Imaging By Tracking Sparse Topological Features In Electron Micrograph Tilt Series
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 242-244
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Management of paediatric laryngotracheal trauma
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 136 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2022, pp. 1125-1129
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the peel number and the leaf-height of Galton–Watson trees
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 June 2022, pp. 68-90
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sequence analyses of mitochondrial gene may support the existence of cryptic species within Ascaridia galli
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 96 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2022, e39
-
- Article
- Export citation
Forecasting the monthly incidence of scarlet fever in Chongqing, China using the SARIMA model
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2022, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Aligning Virtual Care in Canada with the Needs of Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2022, pp. 641-646
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigation on shock-induced separation loss mitigation method considering radial equilibrium in a transonic compressor rotor
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 126 / Issue 1302 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2022, pp. 1394-1413
-
- Article
- Export citation