725 results
Mixed infections with Opisthorchis viverrini and intestinal flukes in residents of Vientiane Municipality and Saravane Province in Laos
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 79 / Issue 3 / September 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 283-289
-
- Article
- Export citation
Emergence of cercariae of Echinostoma caproni and Schistosoma mansoni from Biomphalaria glabrata under different laboratory conditions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 76 / Issue 4 / December 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 369-371
-
- Article
- Export citation
Emergency Department Volumes After State-Wide Lockdown Orders Across the United States During the COVID-19 Pandemic: COVID-19 lockdown and emergency volume
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2024, e29
-
- Article
- Export citation
5 Associations Between Regional Perfusion and Locus Coeruleus MRI Contrast are Moderated by Plasma Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 610-611
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
United we thrive: friendship and subsequent physical, behavioural and psychosocial health in older adults (an outcome-wide longitudinal approach)
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2023, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
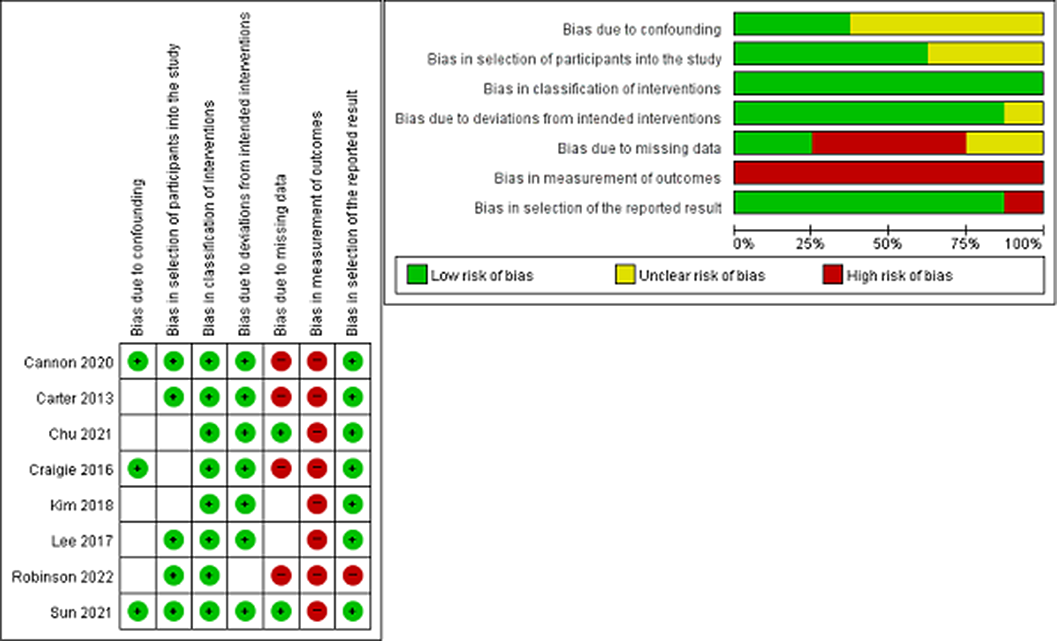
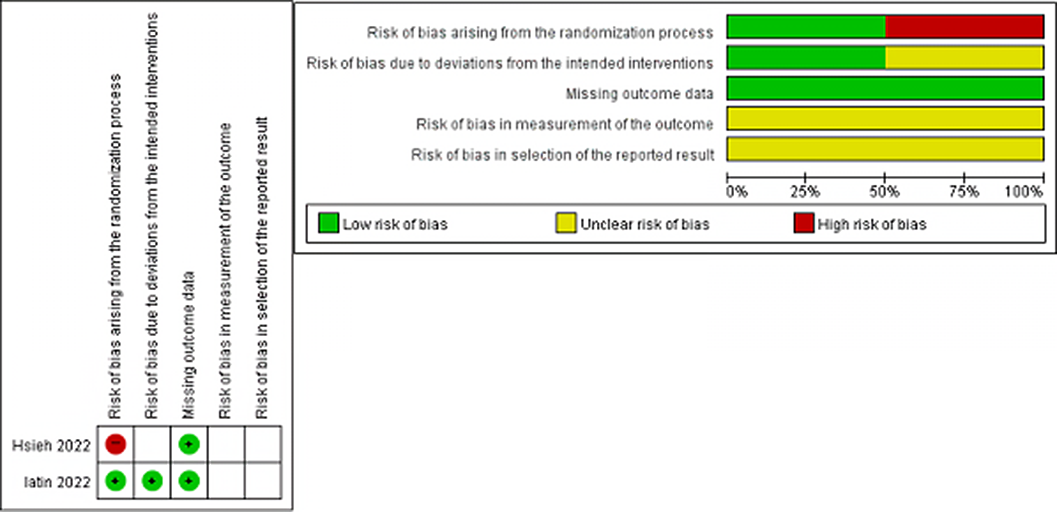
Treatment of hypoplastic left heart syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2023, pp. 659-666
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
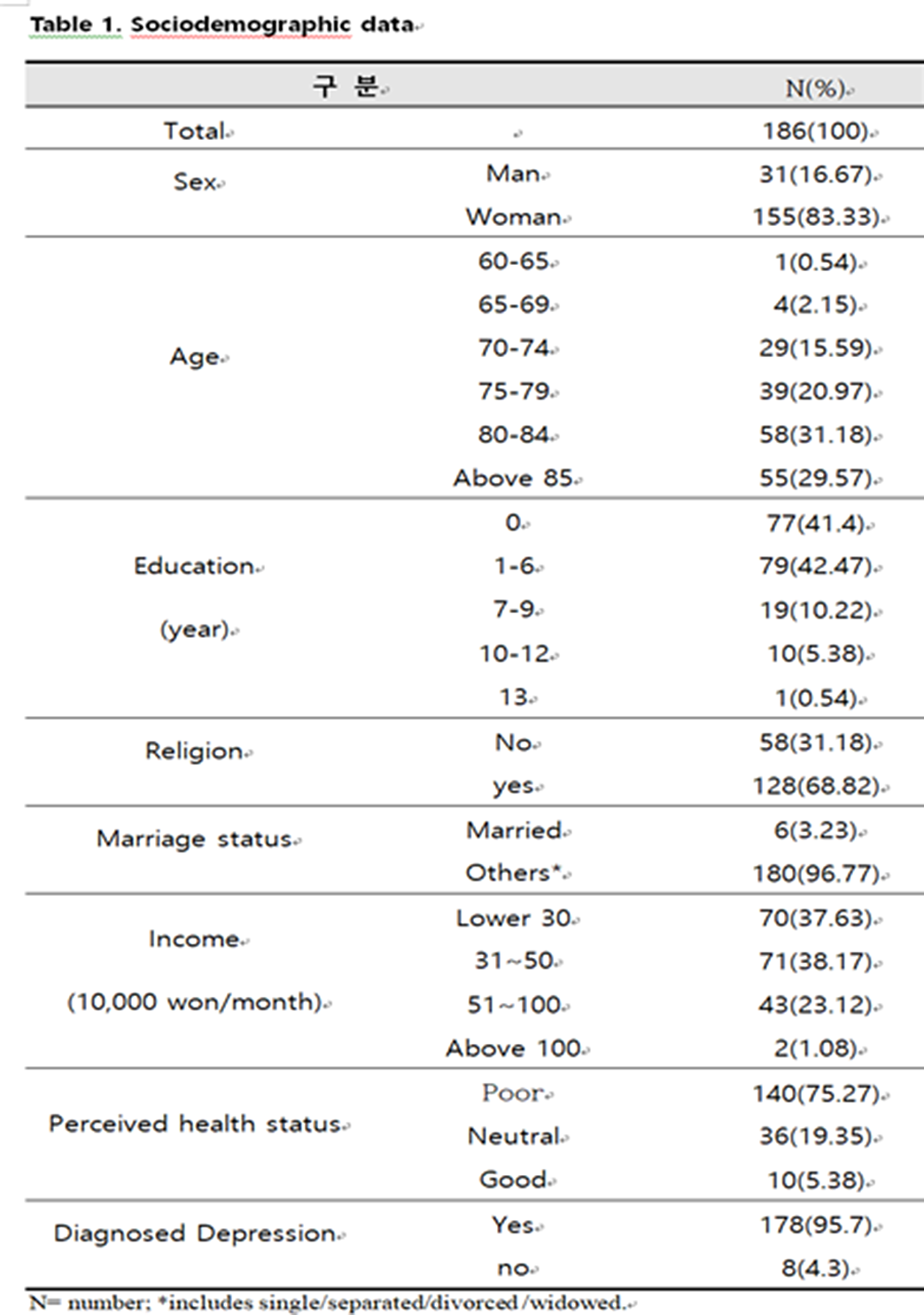
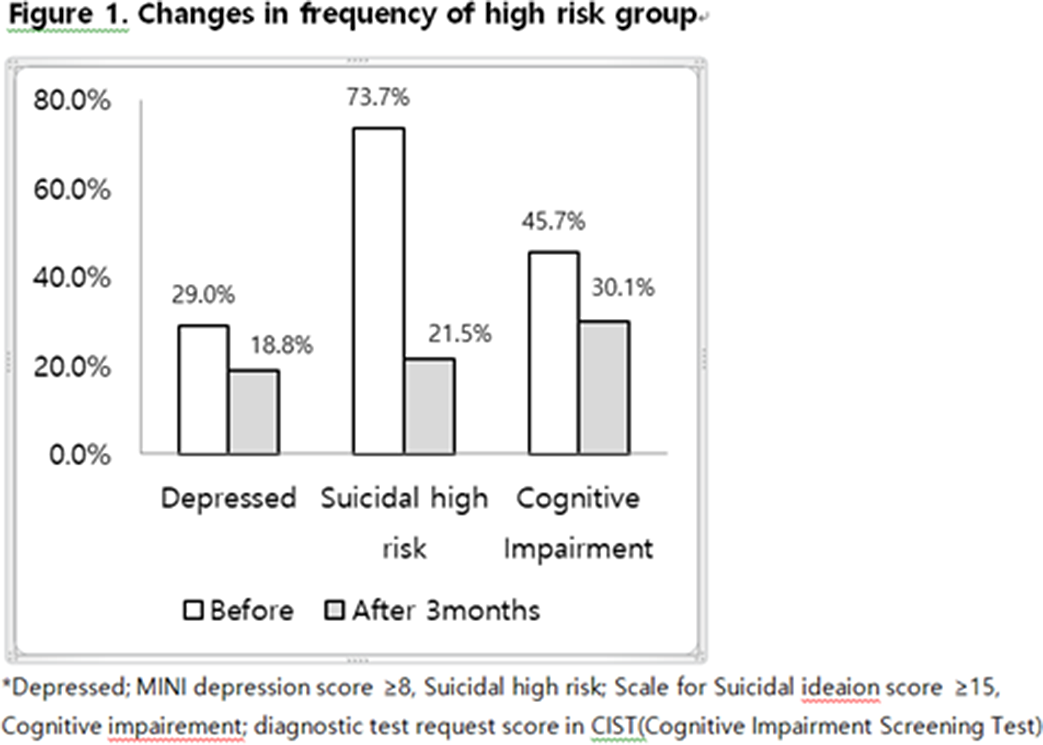
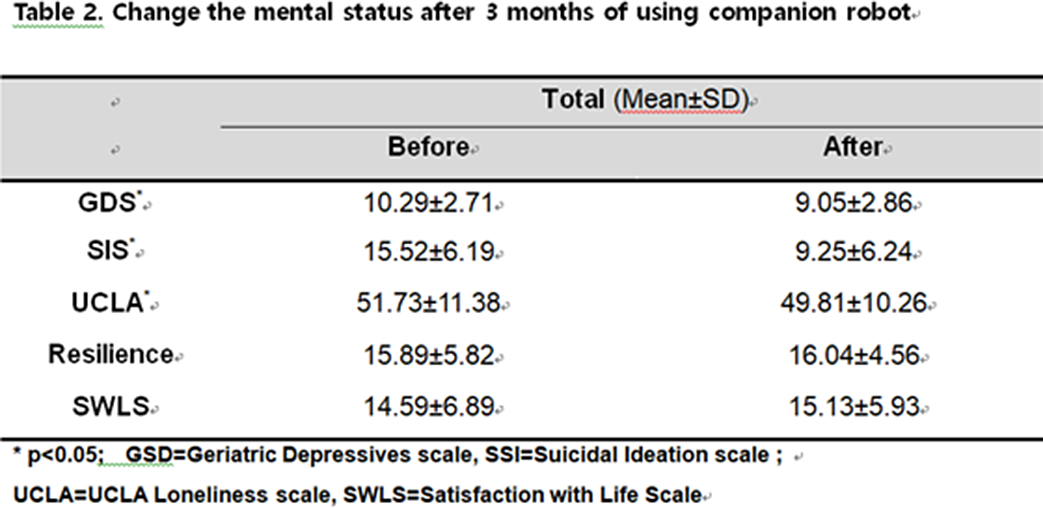
The effect of intervention using an emotional recognition coaching companion robot on the elderly people with depression
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S79-S80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Post-traumatic Stress Disorder in Gangjeong Village Residents, Jeju-do, Korea
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S872
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Self-compassion is associated with the superior longitudinal fasciculus in the mirroring network in healthy individuals
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S550
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Assessing possible moderators on the association between frequency of contact with non-cohabitating adult children and depressive symptoms among community-dwelling older adults
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S222
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
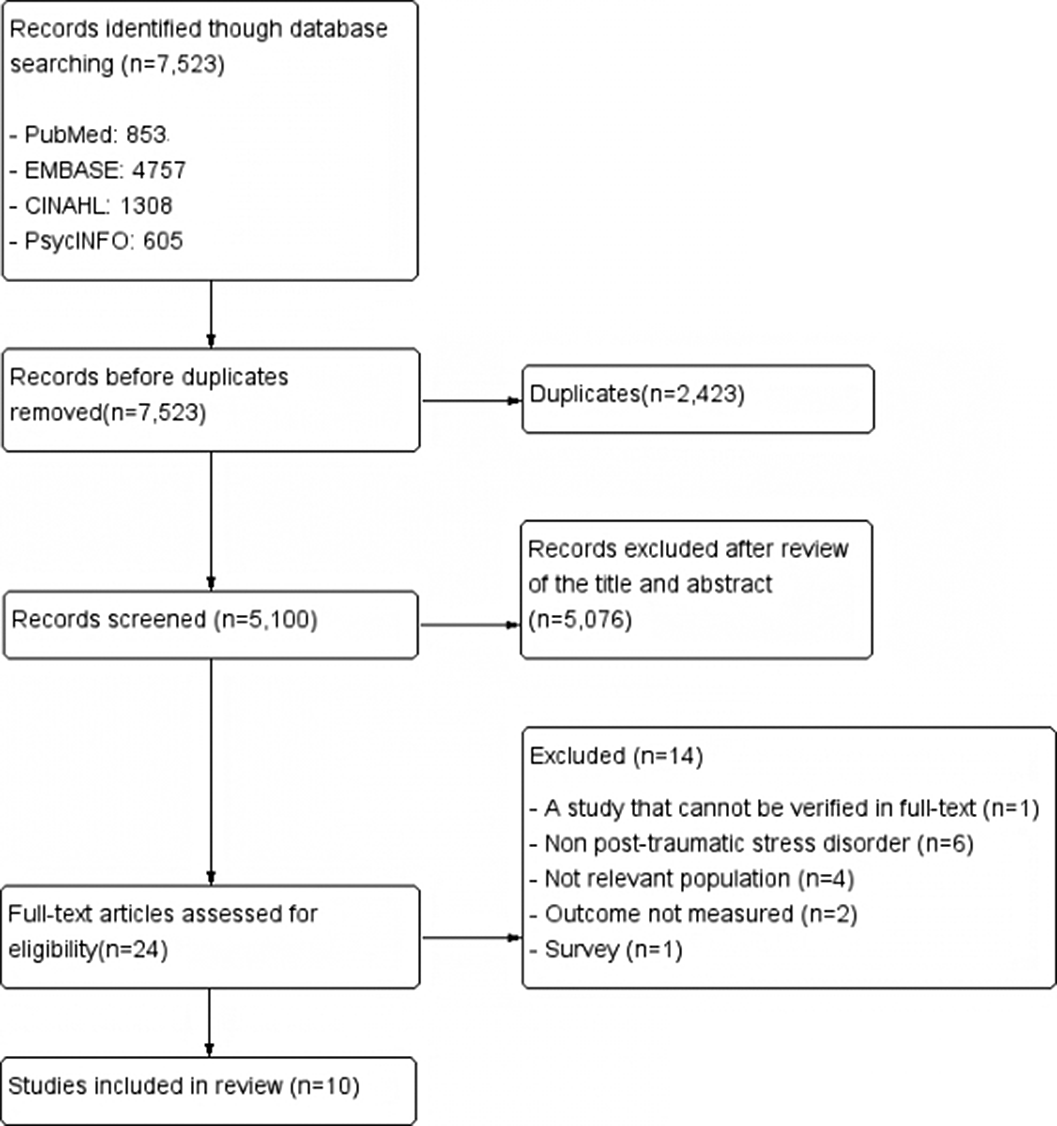
A Systematic Review of the Effect of Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Programs for Nurses
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S977-S978
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
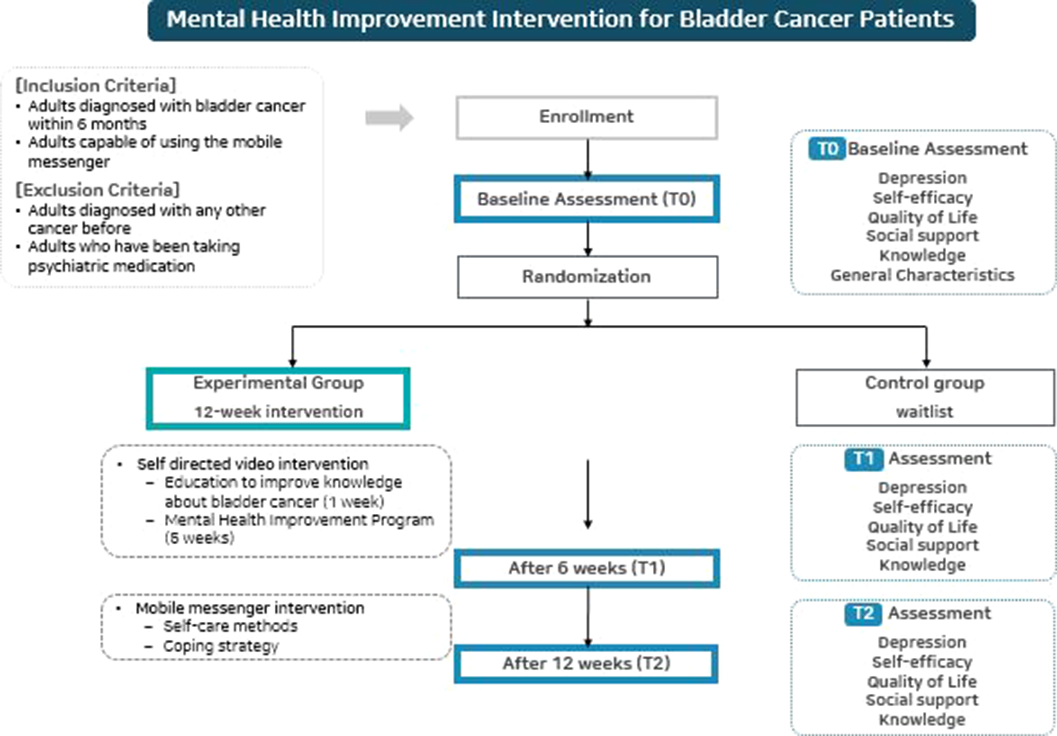
A mobile-based mental health improvement program for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer patients: Program development and feasibility protocol
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S362-S363
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
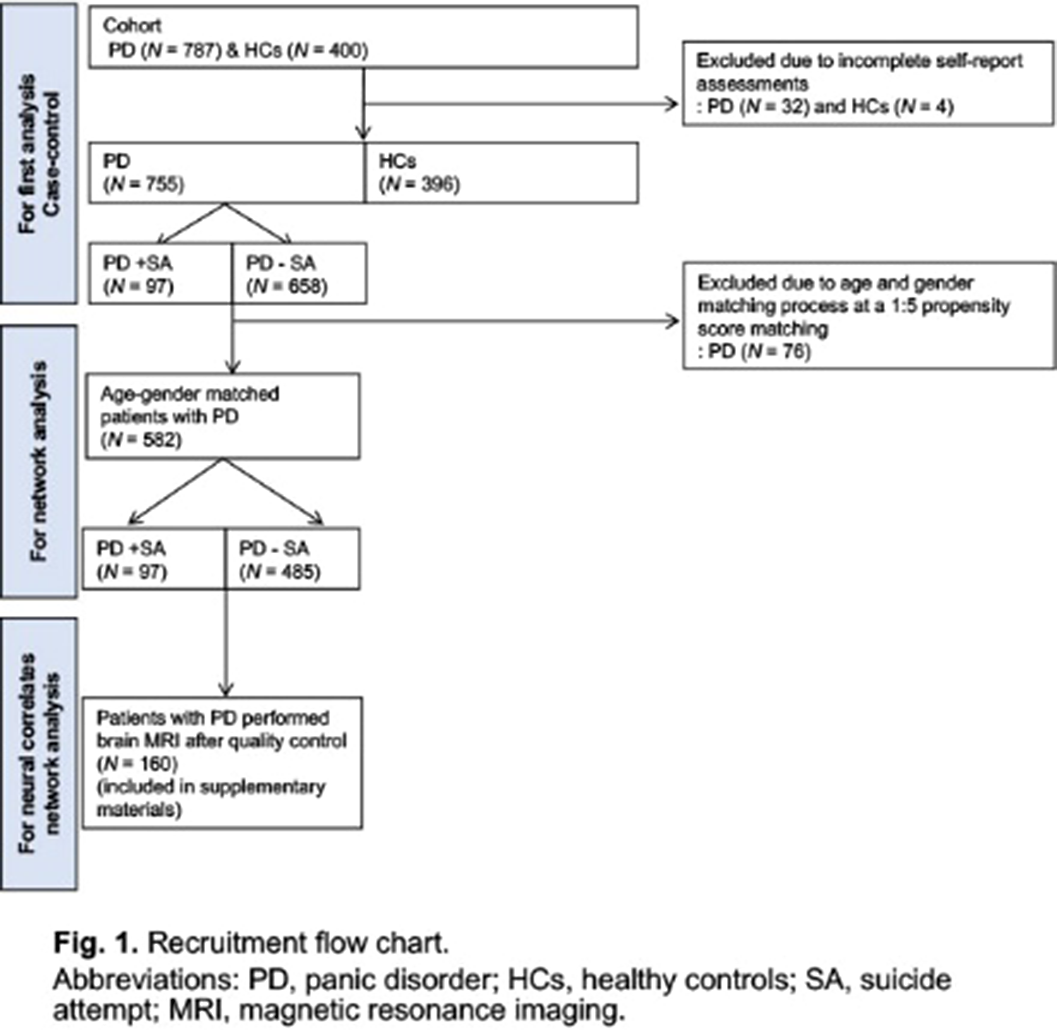
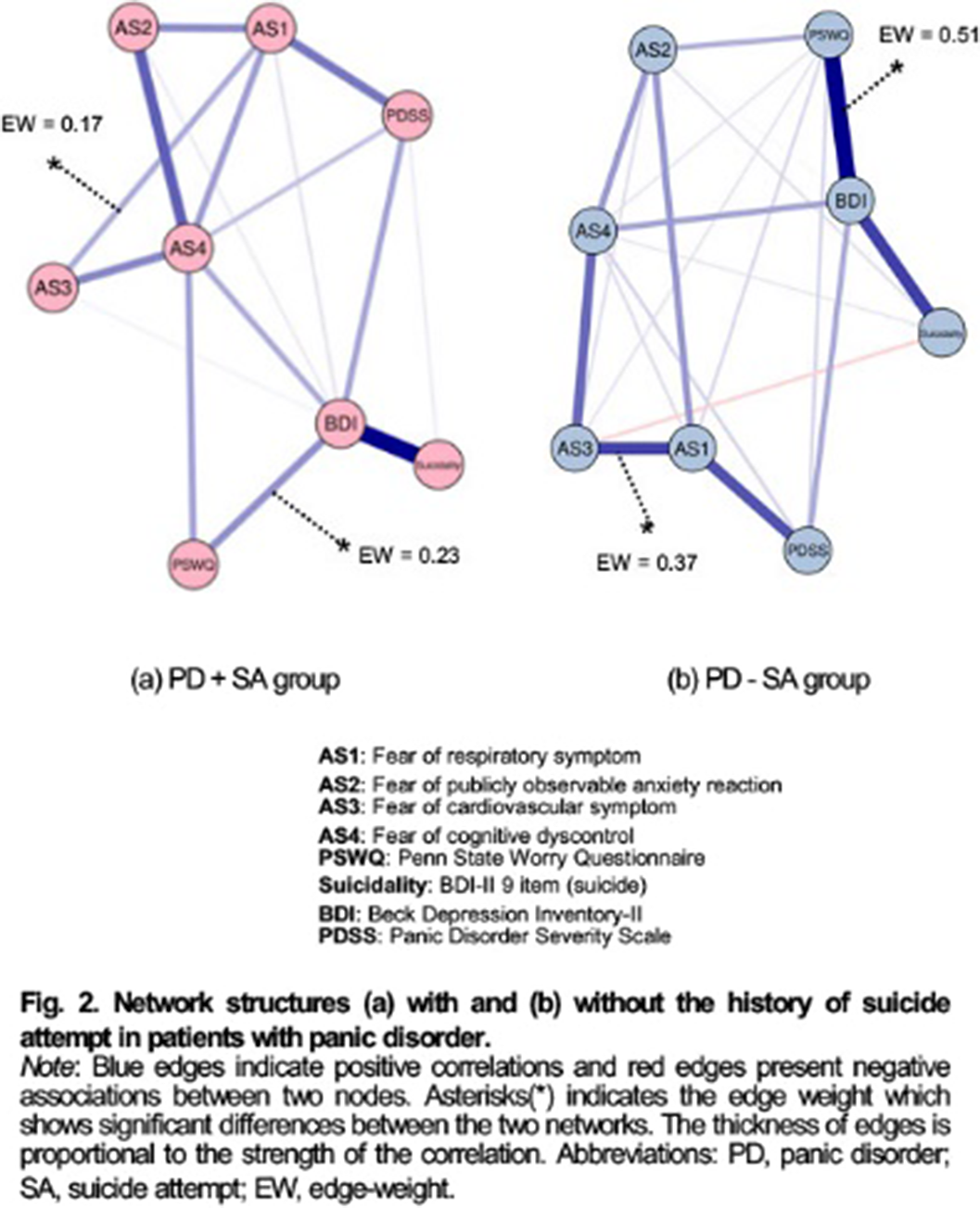
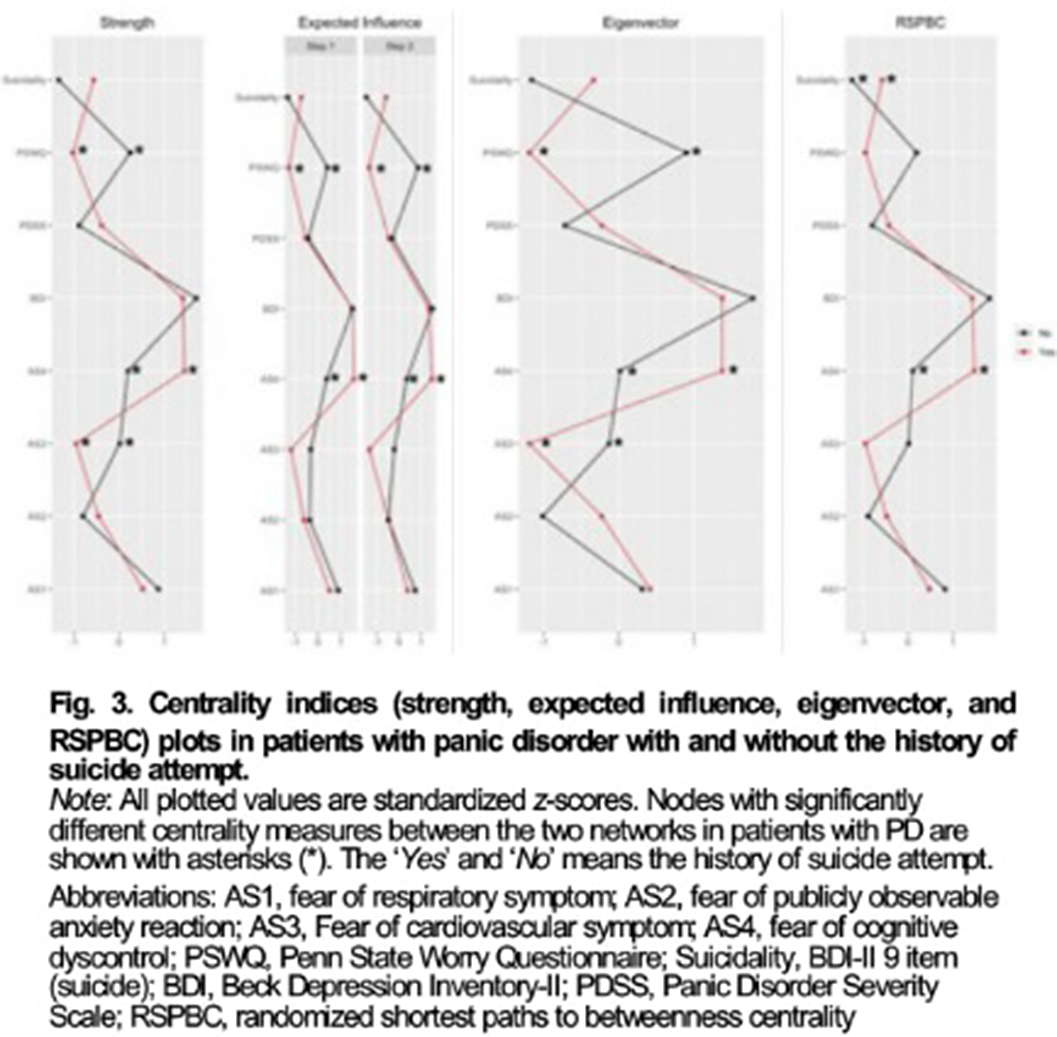
Suicide Attempts in Panic Disorder: Clinical Effects on Treatment Response and Link to Fear of Cognitive Dyscontrol
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S192-S193
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Amisulpride Augmentation in Schizophrenia Patients with Poor Response to Olanzapine: A 4-week, Randomized, Rater-Blind, Controlled, Pilot Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S1093
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Characteristics of patients associated with any outpatient antibiotic prescribing among Medicare Part D enrollees, 2007–2018
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2023, e113
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.065 Comparison in outcomes by sex in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with alteplase versus tenecteplase: a subgroup analysis of AcT
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
‘What does epistemic injustice add? A response to Grim and Aftab’
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 May 2023, pp. 5879-5881
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Aerodynamic characterisation of delta wing unmanned aerial vehicle using non-gradient-based estimator
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1314 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2023, pp. 1435-1451
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between obsessive-compulsive disorder and the risk of schizophrenia using the Korean National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort: a retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2023, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Potential overestimation of cognitive impairment because of hearing loss: impact of test modalities on cognitive test scores
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2023, pp. 845-850
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation