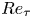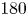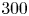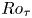166 results
ABSORPTION AND DISTRIBUTION OF ULTRATRACE EXOGENOUS 14C UREA IN RATS
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
The role of the cytochrome P450 superfamily in the skin
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morphology, genetic characterization and phylogeny of Moniliformis tupaia n. sp. (Acanthocephala: Moniliformidae) from the northern tree shrew Tupaia belangeri chinensis Anderson (Mammalia: Scandentia)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, pp. 440-448
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Does CFO Board Membership Benefit Shareholders? The Case of Corporate Acquisitions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2024, pp. 1-28
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation of the psychometrics of the Social Impact Scale and its association with depression among asymptomatic COVID-19 carriers
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, e41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Implementing a continuous quality-improvement framework for tuberculosis infection prevention and control in healthcare facilities in China, 2017–2019
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 651-657
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhancing large-scale motions and turbulent transport in rotating plane Poiseuille flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, A43
-
- Article
- Export citation
OP143 Association Of Different Venous Access Device With Health‑Related Quality Of Life Among Patients With Breast Cancer In China
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PP70 Mapping Of Health Technology Assessment In China: A Comparative Study Between 2016 And 2021
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S71
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PP71 Hospitalization Costs Associated With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer In China: Real World Evidence From Jiangsu
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S71
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Morphology and ASAP analysis of the important zoonotic nematode parasite Baylisascaris procyonis (Stefahski and Zarnowski, 1951), with molecular phylogenetic relationships of Baylisascaris species (Nematoda: Ascaridida)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2023, pp. 200-212
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genomes of the zoonotic parasites Bolbosoma nipponicum and Corynosoma villosum (Acanthocephala: Polymorphida) and the molecular phylogeny of the order Polymorphida
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 45-57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hepatitis B antibody levels after different doses of hepatitis B vaccination: a retrospective study based on hospitalized children
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2023, e186
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Measurements of plasma density profile evolutions with a channel-guided laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2023, e85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inverse correlations between serum carotenoids and respiratory morbidity and mortality: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 11 / 14 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, pp. 1932-1941
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Does pregnancy make women more cautious and calm? The impact of pregnancy on risk decision-making
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 15 / Issue 5 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 807-822
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Does pain make people short-sighted? The impacts of physical and psychological pains on intertemporal choice
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 16 / Issue 4 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 1097-1112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PD12 Quality Assessment Of Health Economic Evaluation On Screening Programs From China
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2022, pp. S93-S94
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Vitamin B12 and gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2022, pp. 1324-1331
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation