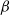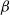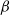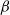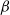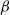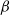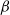644 results
Revealing complexity: beyond the whole—segmentation of hippocampal subfields in adolescents with depression and its relationships with cognition
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, pp. S225-S226
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
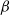 $\beta$-wave-based exploration of sensitive EEG features and classification of situation awareness
$\beta$-wave-based exploration of sensitive EEG features and classification of situation awareness
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effects of surfactants on plunging breakers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2023, R5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
When does education increase political participation? Evidence from Senegal
-
- Journal:
- Political Science Research and Methods / Volume 12 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2023, pp. 354-371
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Output constrained neural adaptive control for a class of KKVs with non-affine inputs and unmodeled dynamics
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1319 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2023, pp. 134-151
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plunging breakers. Part 1. Analysis of an ensemble of wave profiles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 967 / 25 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2023, A35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plunging breakers. Part 2. Droplet generation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 967 / 25 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2023, A36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The interplay of kinematics and aerodynamics in multiple flight modes of a dragonfly
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 967 / 25 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2023, A31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fixed-time cooperative trajectory optimisation strategy for multiple hypersonic gliding vehicles based on neural network and ABC algorithm
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1316 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2023, pp. 1737-1751
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 6 - Health Workforce in Low and Middle Income Countries
- from Section 1 - Analyzing Health Systems: Concepts, Components, Performance
-
-
- Book:
- Making Health Systems Work in Low and Middle Income Countries
- Published online:
- 08 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 29 December 2022, pp 83-101
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Global trends and regional differences in the burden of anxiety disorders and major depressive disorder attributed to bullying victimisation in 204 countries and territories, 1999–2019: an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2022, e85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prescribed-time cooperative guidance with time delay
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1311 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2022, pp. 852-875
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effective aero-optical suppression by steady wall blowing and wall suction schemes for supersonic turbulent boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1312 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 1037-1047
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prediction and copy number variation identification of ZNF146 gene related to growth traits in Chinese cattle
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 404-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acceleration of 60 MeV proton beams in the commissioning experiment of the SULF-10 PW laser
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhancing the take-off performance of hypersonic vehicles using the improved chimp optimisation algorithm
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1311 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2022, pp. 737-753
-
- Article
- Export citation
Endoscopic transoral approach to the parapharyngeal space: technical nuances and preliminary results
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 6 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2022, pp. 678-684
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
P.153 Traumatic spinal cord injuries among indigenous and non-indigenous peoples of Canada
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue s1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, p. S47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Mental disorder symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic in Latin America – a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation