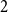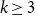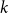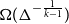1751 results
Neoadjuvant radiotherapy and wound complication: literature review and review of single surgeon series of myxoid liposarcoma treated with neoadjuvant radiotherapy followed by surgery
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice / Volume 23 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2024, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Weston Park Music Collection: Five Generations of Family Music-Making in Eighteenth-Century Staffordshire
-
- Journal:
- Royal Musical Association Research Chronicle ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Harold S. Wechsler and Steven J. Diner. Unwelcome Guests: A History of Access to American Higher Education Baltimore: John Hopkins University Press, 2019. 225 pp.
-
- Journal:
- History of Education Quarterly / Volume 64 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, pp. 224-227
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Metastability in Near-Surface Rocks of Minerals in The System Al2O3-SiO2-H2O
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 39 / Issue 3 / June 1991
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 225-233
-
- Article
- Export citation
6 - “Thynke nat the contrary”: Field Notes in the Ecology of Medieval Romance
-
-
- Book:
- Form and Power in Medieval and Early Modern Literature
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 17 May 2024
- Print publication:
- 05 March 2024, pp 107-120
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Mineral Metastability in the System Al2O3-SiO2-H2O: A Reply
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 42 / Issue 1 / February 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 102-105
-
- Article
- Export citation
Elasmobranch diversity around the southern Caribbean island of Tobago: opportunities for conservation in a regional trade hub
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Functional properties of cream and butter oil from milk of Holstein cows abomasally infused with increasing amounts of high-oleic sunflower fatty acids
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Triarchic traits as risk versus protective factors for ADHD symptomatology: A prospective longitudinal investigation
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
73 Identification of 24-Month Cognitive Trajectories Among Clinical High Risk for Psychosis (CHR-P) Using Latent Class Mixture Modeling
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 857-858
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Physician perceptions of barriers to infection prevention and control in labor and delivery
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2023, pp. 483-490
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
GOSPEL WRITERS AND CLASSICAL POETS - (D.R.) MacDonald Synopses of Epic, Tragedy, and the Gospels. Volume 1: Mimetic Synopsis of Four Synoptic Gospels (Q+, Mark, Matthew, and Luke). Imitations of Deuteronomy, Homer, and Athenian Tragedies. Volume 2: Mimetic Syncrisis of the Acts of the Apostles. Imitations of Homer and Euripides and Rivalry with the Aeneid. Volume 3: Mimetic Synopsis of Three Gospels of John. Imitations of the Synoptics and Euripides’ Bacchae. Pp. viii + 564, colour ills. Claremont, CA: Mimesis Press, 2022. Paper, £36.51. ISBN: 979-8-9867801-1-5.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 312-314
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microbiological characteristics, transmission routes, and mitigation measures in bronchoscope-associated investigations: Summary of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) consultations, 2014–2022
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 2052-2055
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Healthcare-associated Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections in the United States, 2018–2022
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
CDC consultations related to ophthalmologic practices and settings, 2016–2021
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s120
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Outbreak of Burkholderia multivorans among patients at two acute-care hospitals in California, August 2021–July 2022
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s89-s90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
4 - No-Boundary Course Developments
-
-
- Book:
- Integrative Bioinformatics for Biomedical Big Data
- Published online:
- 14 September 2023
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2023, pp 45-66
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
5 - No-Boundary Thinking for Transcriptomics and Proteomics Big Data
-
-
- Book:
- Integrative Bioinformatics for Biomedical Big Data
- Published online:
- 14 September 2023
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2023, pp 67-86
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
On the zeroes of hypergraph independence polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2023, pp. 65-84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
New toolkit for Nature-Positive Enterprise development
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation