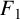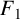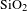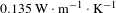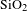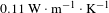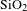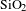25 results
NEW CONGRUENCES FOR THE TRUNCATED APPELL SERIES
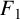 $F_1$
$F_1$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of dietary oxidative balance score and sleep duration with the risk of mortality: prospective study in a representative US population
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, pp. 2066-2075
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protective effect of antioxidants on cardiac function in adult offspring exposed to prenatal overnutrition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 13 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2022, pp. 741-749
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of folic acid and riboflavin on growth performance, nutrient digestion and rumen fermentation in Angus bulls
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2022, pp. 1-9
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of folic acid and cobalt sulphate supplementation on growth performance, nutrient digestion, rumen fermentation and blood metabolites in Holstein calves
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 June 2021, pp. 1313-1319
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hypothalamic regulation of energy homoeostasis when consuming diets of different energy concentrations: comparison between Tibetan and Small-tailed Han sheep
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2021, pp. 1132-1142
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of spicy food flavour and intake frequency with blood lipid levels and risk of abnormal serum lipid levels in Chinese rural population: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 18 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2021, pp. 6201-6210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The association between dietary patterns with type 2 diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes in the Henan rural cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 16 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 January 2021, pp. 5443-5452
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparison between Tibetan and Small-tailed Han sheep in adipocyte phenotype, lipid metabolism and energy homoeostasis regulation of adipose tissues when consuming diets of different energy levels
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 7 / 14 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2020, pp. 668-680
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Initial Performance Evaluation of Precise Point Positioning with Triple-Frequency Observations from BDS-2 and BDS-3 Satellites
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 73 / Issue 4 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2020, pp. 763-775
- Print publication:
- July 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tibetan sheep have a high capacity to absorb and to regulate metabolism of SCFA in the rumen epithelium to adapt to low energy intake
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 123 / Issue 7 / 14 April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2019, pp. 721-736
- Print publication:
- 14 April 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reproducibility and validity of an FFQ in the Henan Rural Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2019, pp. 34-40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Designing Energy Materials via Atomic-resolution Microscopy and Spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 25 / Issue S2 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 1998-1999
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A multiplex PCR for the identification of Echinococcus multilocularis, E. granulosus sensu stricto and E. canadensis that infect human
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 146 / Issue 12 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 July 2019, pp. 1595-1601
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Prevalence of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Among Survivors After a Typhoon or Hurricane: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 13 / Issue 5-6 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 June 2019, pp. 1065-1073
-
- Article
- Export citation
A free-rotating ball-shaped transmitting coil with wireless power transfer system for robot joints
-
- Journal:
- Wireless Power Transfer / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2019, pp. 26-40
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets incorporated antireflective silica coating with enhanced laser-induced damage threshold
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 6 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2018, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Middle Ordovician actinocerid nautiloids (Cephalopoda) from Xainza County, Tibet, western China, and their paleogeographic implications
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 92 / Issue 3 / May 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2018, pp. 398-411
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reproducibility and validity of dietary patterns identified using factor analysis among Chinese populations
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 116 / Issue 5 / 14 September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2016, pp. 842-852
- Print publication:
- 14 September 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation