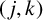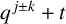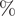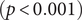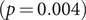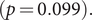269 results
CHARACTERISTIC POLYNOMIALS OF THE MATRICES WITH
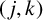 $(\,j,k)$-ENTRY
$(\,j,k)$-ENTRY 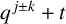 $q^{\,j\pm k}+t$
$q^{\,j\pm k}+t$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
High efficiency, high-resolution multiple monochromatic imaging based on multilayers mirrors array for laser-plasma diagnostic of X-ray continuum emission
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in several regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Super-efficient Reduction of 4-nitrophenol Using Raw Pelagic Clays as Catalysts
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 745-759
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spicy food consumption reduces the risk of ischaemic stroke: a prospective study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 10 / 28 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2024, pp. 1777-1785
- Print publication:
- 28 May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Distribution and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements (REE) in the Ion Adsorption-type REE Deposit (IAD) at Maofeng Mountain, Guangzhou, China
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 340-361
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterization of Energetic Protons Generated in the ShenGuang-II UP Petawatt Laser Interactions with Foil Targets
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Intelligent Optimization of Parameters for Tens of MA-Class Z-Pinch Accelerators
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PP70 Mapping Of Health Technology Assessment In China: A Comparative Study Between 2016 And 2021
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S71
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dynamic structure–function coupling across three major psychiatric disorders
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 8 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2023, pp. 1629-1640
-
- Article
- Export citation
Theoretical analysis of frequency modulation-to-amplitude modulation on the final optics and target of the SG II-Up laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Interesting and impressive: exploring design factors for product graphics interchange format to enhance engagement
-
- Journal:
- Design Science / Volume 9 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2023, e33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Late Quaternary glaciations in the Taniantaweng Mountains
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 117 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 3-18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Conditional analysis on extreme wall shear stress and heat flux events in compressible turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, A38
-
- Article
- Export citation
Social mixing and network characteristics of COVID-19 patients before and after widespread interventions: A population-based study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, e141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factors Associated with Symptom-to-Door Delay in Patients with ST-Segment Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2023, pp. 485-494
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Weak random periodic solutions of random dynamical systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2023, pp. 137-151
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Early-initiated childhood reading for pleasure: associations with better cognitive performance, mental well-being and brain structure in young adolescence
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2023, pp. 359-373
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation