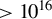921 results
Chapter 8 - Psychopharmacology of Chronic Aggression and Violence in Forensic Settings
-
-
- Book:
- Seminars in Forensic Psychiatry
- Print publication:
- 13 June 2024, pp 208-228
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Boundary mixing. Part 2. The impact of ventilation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 985 / 25 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, A24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A coordinated switch in sucrose and callose metabolism enables enhanced symplastic unloading in potato tubers
-
- Journal:
- Quantitative Plant Biology / Volume 5 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
439 Extracellular-in-frame deletions and kinase domain duplications are novel, gain-of-function mutations in fibroblast growth factor receptor genes in cancer
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 130
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A new MIS 5 to MIS 2 speleothem record from Sandkraal Cave on the South African Cape south coast
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 118 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2024, pp. 142-161
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incidence of mental health diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multinational network study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Autonomous predictive maintenance of quadrotor UAV with multi-actuator degradation
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
- Export citation
China’s prevention and control experience of echinococcosis: A 19-year retrospective
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effect of extrusion screw speeds on molecular weight and immune responses of water soluble arabinoxylans from rice bran
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E376
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Influence of Octahedral Cation Distribution in Montmorillonite on Interlayer Hydrogen Counter-Ion Retention Strength via First-Principles Calculations
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 439-448
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ion-Exchange Modeling of Divalent Cation Adsorption on SWy-3 Montmorillonite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 167-187
-
- Article
- Export citation
Correction to: Influence of Octahedral Cation Distribution in Montmorillonite on Interlayer Hydrogen Counter-Ion Retention Strength Via First-Principles Calculations
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, p. 449
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ion-Exchange Modeling of Monovalent Alkali Cation Adsorption on Montmorillonite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 68 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 476-490
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fabrication of Anthocyanin/Montmorillonite Hybrid Pigments to Enhance Their Environmental Stability and Application in Allochroic Composite Films
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 142-151
-
- Article
- Export citation
17 The Chinese Version of Craft Story Recall: A Preliminary Study on the Diagnostic Values of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 700-701
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Boundary mixing. Part 1. Transport of buoyancy and passive tracer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 976 / 10 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, A23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Host response of Nicotiana benthamiana to the parasitism of five populations of root-lesion nematode, Pratylenchus coffeae, from China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 97 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, e73
-
- Article
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reciprocal relationships between self-esteem, coping styles and anxiety symptoms among adolescents: Between-person and within-person effects
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S748
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Role of bilingual experience in children's context-sensitive selective trust strategies
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2023, pp. 95-106
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation