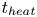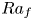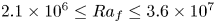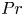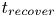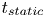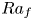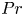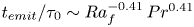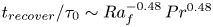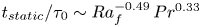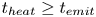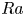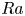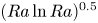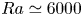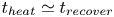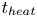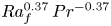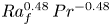63 results
Considering climate change impact on the global potential geographical distribution of the invasive Argentine ant and little fire ant
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in several regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Formation and evolution of laminar thermal structures: correlation to the thermal boundary layer and effects of heating time
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, A60
-
- Article
- Export citation
Analysis of the guiding effect of image dissemination on students with autism
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Guidance of creative design and delivery of information flow advertising to consumer anxiety
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. S106-S107
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Foreground-background salience effect in traffic risk communication
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / January 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 83-89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Connectome-based prediction of eating disorder-associated symptomatology
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2022, pp. 5786-5799
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality in patients with COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, e106
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Systematic paleontology, acritarch biostratigraphy, and δ13C chemostratigraphy of the early Ediacaran Krol A Formation, Lesser Himalaya, northern India
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2022, pp. 1-62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of dietary tryptophan on muscle growth, protein synthesis and antioxidant capacity in hybrid catfish Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. 1761-1773
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations between hemispheric asymmetry and schizophrenia-related risk genes in people with schizophrenia and people at a genetic high risk of schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 1 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 April 2021, pp. 392-400
- Print publication:
- July 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A simple way to minimize cross infection from tear droplets during noncontact air-puff tonometry
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 10 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2020, pp. 1296-1297
- Print publication:
- October 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of the ZM61 alloy sheets under different pre-rolling and high strain rate rolling temperatures
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 14 / 28 July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2020, pp. 1817-1824
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plasma magnesium and the risk of new-onset hyperuricaemia in hypertensive patients
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 March 2020, pp. 156-163
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of dietary threonine on growth performance and muscle growth, protein synthesis and antioxidant-related signalling pathways of hybrid catfish Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 123 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2019, pp. 121-134
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Radiocarbon dating of Chinese Ancient Tea Trees
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 61 / Issue 6 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 October 2019, pp. 1741-1748
- Print publication:
- December 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
MIR137 polygenic risk is associated with schizophrenia and affects functional connectivity of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 9 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 June 2019, pp. 1510-1518
-
- Article
- Export citation
Underground nuclear astrophysics experiment JUNA in China
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S350 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2020, pp. 313-320
- Print publication:
- April 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Late onset of the Holocene rainfall maximum in northeastern China inferred from a pollen record from the sediments of Tianchi Crater Lake
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 92 / Issue 1 / July 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2019, pp. 133-145
-
- Article
- Export citation