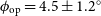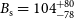310 results

Beyond Civility in Social Conflict
- Dialogue, Critique, and Religious Ethics
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- June 2024
- Print publication:
- 27 June 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Reduction of airborne and surface-borne bacteria in a medical center burn intensive care unit using active, upper-room, germicidal ultraviolet (GUV) disinfection
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2023, pp. 367-373
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The first weed management textbook in the United States (part 2)
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 38 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2023, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The first weed science textbooks in the United States (Part 1)
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 37 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 657-669
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Observation of subcritical shocks in a collisional laboratory plasma: scale dependence near the resistive length
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2023, 915890401
-
- Article
- Export citation
Computerized adaptive test strategies for the matrix reasoning subtest of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, 4th Edition (WAIS-IV)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2023, pp. 152-161
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mental health of children and young people aged 5-16 in England: socio-demographic and clinical characteristics associated with support and service contact
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S582
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
An energetic signature for breaking inception in surface gravity waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 959 / 25 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2023, A33
-
- Article
- Export citation
Role of the overshoot in the shock self-organization
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2023, 905890201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 4 - The Sperm’s Role in Embryo Development
-
-
- Book:
- Manual of Embryo Selection in Human Assisted Reproduction
- Published online:
- 26 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2023, pp 31-42
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Compounding and complementary carnivores: Australian bird species eaten by the introduced European red fox Vulpes vulpes and domestic cat Felis catus
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 32 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2021, pp. 506-522
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ultrastructural characterization of host–parasite interactions of Plasmodium coatneyi in rhesus macaques
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 149 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2021, pp. 161-170
-
- Article
- Export citation
A broadband radio view of transient jet ejecta in the black hole candidate X-ray binary MAXI J1535–571
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2021, e045
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cardiac echocardiogram findings of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2-associated multi-system inflammatory syndrome in children – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2021, p. 727
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gender, age at onset, and duration of being ill as predictors for the long-term course and outcome of schizophrenia: an international multicenter study
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 27 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2021, pp. 716-723
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cardiac echocardiogram findings of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2-associated multi-system inflammatory syndrome in children
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2021, pp. 718-726
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enabling a Paradigm Shift in CryoEM Sample Preparation with chameleon
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 524-525
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
When Managers Become Robin Hoods: A Mixed Method Investigation
-
- Journal:
- Business Ethics Quarterly / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2021, pp. 209-242
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rationale and Design of the National Neuropsychology Network
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 28 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2021, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparison of meat versus soya based high-protein diets on faecal microbiota and microbial metabolites
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 79 / Issue OCE3 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2020, E781
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation