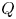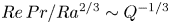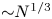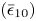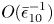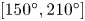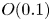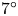161 results
Can Meta-Omics Revolutionize Our Understanding of Rumen Methane Emissions?
-
- Journal:
- Animal Nutriomics / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2024, pp. 1-42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Transport of inertial spherical particles in compressible turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 990 / 10 July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2024, A5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental study of a single bubble's motion in a liquid metal under a horizontal magnetic field
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 988 / 10 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, A21
-
- Article
- Export citation
The melanin pigment gene black mediates body pigmentation and courtship behaviour in the German cockroach Blattella germanica
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, pp. 271-280
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the effects of the timing of an intense cyclone on summertime sea-ice evolution in the Arctic
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
98 The Crosstalk between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Preterm Infants with Pain/Stress in the NICU
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Molecular mechanisms of cytochrome P450-mediated detoxification of tetraniliprole, spinetoram, and emamectin benzoate in the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 159-171
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of horizontal magnetic fields on turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a cuboid vessel with aspect ratio Γ = 5
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, A24
-
- Article
- Export citation
Principle of fundamental resonance in hypersonic boundary layers: an asymptotic viewpoint
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, A30
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unraveling the link between childhood maltreatment and depression: Insights from the role of ventral striatum and middle cingulate cortex in hedonic experience and emotion regulation
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
High-Temperature Transformation of Asbestos Tailings by Carbothermal Reduction
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 61 / Issue 1 / February 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 75-82
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Charge State of Protons with 90 and 100 keV Energies Decelerated in Hydrogen Plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ontogenetic morphological changes of the venom apparatus in 4 eupelmid egg parasitoids
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 185-190
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prospect of ultrahigh-resolution fast neutron absorption spectroscopy based on a laser plasma electron accelerator
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of compliant coating on Mack-mode evolution in hypersonic boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, A1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of cone rotation on the nonlinear evolution of Mack modes in supersonic boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2023, A4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Instability evolution of a shock-accelerated thin heavy fluid layer in cylindrical geometry
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 969 / 25 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2023, A6
-
- Article
- Export citation
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE CHARGE-EXCHANGE CROSS-SECTIONS OF LOW-ENERGY CARBON IONS IN HELIUM AT GXNU
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in breast cancer cells and its effect on reversing tumour drug resistance by alkaloids extracted from traditional Chinese medicine
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 25 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 June 2023, e21
-
- Article
- Export citation