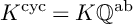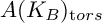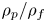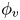125 results

Spectral and Spectral Element Methods for Fractional Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- November 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Decay rate of homogeneous isotropic turbulence laden with finite-size particles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 993 / 25 August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2024, A15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clay and Fe (oxyhydr)oxide mineralogy in the basalt weathering profile in Hainan (southern China): implications for pedogenesis process
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 72 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
15 - State-Led Community (Dis)empowerment in China
- from Part III - Civil Society and Coalitions
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Community Empowerment
- Published online:
- 18 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 25 April 2024, pp 389-412
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Preferential accumulation of finite-size particles in near-wall streaks
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2024, A38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of Calcination Temperature on the Structure of Chitosan-Modified Montmorillonites and their Adsorption of Aflatoxin B1
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 357-366
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON THE ESSENTIAL TORSION FINITENESS OF ABELIAN VARIETIES OVER TORSION FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 253 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 91-127
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Population dynamics and conservation status of the white-headed langur in the Chongzuo forest fragments, Guangxi, China
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Parameterization of turbulence modulation by finite-size solid particles in forced homogeneous isotropic turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 963 / 25 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2023, A6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Three-dimensional sedimentation patterns of two interacting disks in a viscous fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 960 / 10 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, A25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mechanisms and models of particle drag enhancements in turbulent environments
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 959 / 25 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2023, A30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dose–response relationship between dietary inflammatory index and diabetic kidney disease in US adults
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2022, pp. 611-619
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Folic acid supplementation in pregnant women with hepatitis B surface antigen improves infant hepatitis B surface antibody mediated by infant IL-4
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 10 / 28 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2022, pp. 1812-1819
- Print publication:
- 28 May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Critically Endangered dragonfly Libellula angelina is losing its habitat to urbanization in East Asia
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of dietary intake of branched-chain amino acids with long-term risks of CVD, cancer and all-cause mortality
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 12 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2021, pp. 3390-3400
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary iron intake and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged and older adults in urban China: a prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 7 / 14 October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2020, pp. 1091-1099
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary patterns and their associations with the metabolic syndrome and predicted 10-year risk of CVD in northwest Chinese adults
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2020, pp. 913-922
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nanoscale TiO2 coating improves water stability of Cs2SnCl6
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2020, pp. 687-694
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Liver X receptor α participates in LPS-induced reduction of triglyceride synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 87 / Issue 4 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2020, pp. 456-462
- Print publication:
- November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation