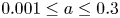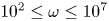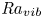144 results
Air-filled substrate integrated waveguide bandpass filter based on miniaturized non-resonant node structure
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 July 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Long-term outcomes of repair in children with total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unifying constitutive law of vibroconvective turbulence in microgravity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, A14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Long-term outcomes after the arterial switch operation
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Innovation in surgical treatment of hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy in children
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Individualised surgical treatment strategy for subaortic stenosis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Gender, Competition, and Performance: International Evidence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, pp. 1-63
-
- Article
- Export citation
OP04 The Efficacy Of Segmentectomy And Lobectomy For Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, pp. S1-S2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Anatomical studies and early results on endoscopic transoral medial pterygomandibular fold approach to salvage retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 540-547
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flow structure transition in thermal vibrational convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, A29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
New insight into inheritance pattern of seed coat colour in adzuki bean
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 298-303
-
- Article
- Export citation
On shock induced aerobreakup of a wall-attached droplet
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, A31
-
- Article
- Export citation
Semantic 3D city interfaces—Intelligent interactions on dynamic geospatial knowledge graphs
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The psychology and policy of overcoming economic inequality
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 46 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2023, e174
-
- Article
- Export citation
A 115 ps, 100 Hz high-beam-quality laser based on transient stimulated Brillouin scattering pulse compression
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optical rectification in 4H-SiC: paving the way to generate strong terahertz fields with ultra-wide bandwidth
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 June 2023, e62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Effects of a U.S. Approach to Enforcement: Evidence from China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 59 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, pp. 121-156
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Appetite hormone dysregulation, body mass index, and emotional dysregulation in nonobese adolescents with first-episode schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder: a cross-sectional association study
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2023, pp. 629-636
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparative effectiveness of psychotherapies in adults with posttraumatic stress disorder: a network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 13 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 6376-6388
-
- Article
- Export citation