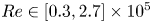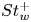214 results
Generation of energetic electrons by an electron cyclotron wave through stochastic heating in a spherical tokamak
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2023, 905890603
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of backpressure on unstart and restart characteristics of a supersonic inlet
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1316 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, pp. 1774-1792
-
- Article
- Export citation
Post-operative vestibular and equilibrium evaluation in patients with cholesteatoma-induced labyrinthine fistulas
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, pp. 16-21
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
UAV swarm collaborative coverage control using GV division and planning algorithm
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1309 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2022, pp. 446-465
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of nitrogen application rates on the spatio-temporal variation of leaf SPAD readings on the maize canopy
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 1-2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2022, pp. 32-44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spatial epidemiological characteristics and exponential smoothing model application of tuberculosis in Qinghai Plateau, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2022, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Empowering families facing end-stage nonmalignant chronic diseases with a holistic, transdisciplinary, community-based intervention: 3 months outcome of the Life Rainbow Program – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, p. 640
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Flow structure around a low-drag Ahmed body
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 913 / 25 April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2021, A21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Health and social care service utilisation and associated expenditure among community-dwelling older adults with depressive symptoms
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 30 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2021, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Respiratory failure among patients with COVID-19 in Jiangsu province, China: a multicentre retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2021, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Empowering families facing end-stage nonmalignant chronic diseases with a holistic, transdisciplinary, community-based intervention: 3 months outcome of the Life Rainbow Program
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 December 2020, pp. 530-539
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory: A kilohertz-band gravitational-wave detector in the global network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiological characteristics and spatial−temporal analysis of COVID-19 in Shandong Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2020, e141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic addiction risk score analysis: hypodopaminergic polymorphic risk alleles in polydrug addicted males and meso-limbic dopaminergic agonistic activation by neuroadaptagen amino-acid therapy
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / March 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 803
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
GABRB2 in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: Disease Association, Gene Expression and Clinical Correlations
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 24 / Issue S1 / January 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, 24-E1123
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
1356 – Early Attrition And Remission Outcomes Of Depression: An 18-month Nationwide Population-based Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, 28-E691
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The alienation of affection toward parents and influential factors in Chinese left-behind children
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 39 / January 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, pp. 114-122
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spatial dynamics of a nonlocal model with periodic delay and competition
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 31 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2020, pp. 1070-1100
-
- Article
- Export citation