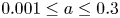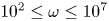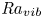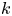138 results
Unifying constitutive law of vibroconvective turbulence in microgravity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, A14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bifurcation of equilibrium positions for ellipsoidal particles in inertial shear flows between two walls
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2024, A47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Meaning-focused foreign language instruction via telepresence robots: A geosemiotic analysis
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spicy food consumption reduces the risk of ischaemic stroke: a prospective study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 10 / 28 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2024, pp. 1777-1785
- Print publication:
- 28 May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Treatment of Municipal Landfill Leachate with Organically Modified Bentonite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 518-524
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flow structure transition in thermal vibrational convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, A29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nanosecond laser conditioning of multilayer dielectric gratings for picosecond–petawatt laser systems
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, e89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thulium-doped all-PM fiber chirped pulse amplifier delivering 314 W average power
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Population dynamics and conservation status of the white-headed langur in the Chongzuo forest fragments, Guangxi, China
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Competition relations between selected microalgae and bloom-forming Ulva prolifera
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 103 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, e43
-
- Article
- Export citation
High-power femtosecond laser generation from an all-fiber linearly polarized chirped pulse amplifier
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2023, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Serum levels of n-3 PUFA and colorectal cancer risk in Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 7 / 14 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2023, pp. 1239-1249
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparison of ventricular synchrony in children with left bundle branch area pacing and right ventricular septal pacing
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2023, pp. 2078-2086
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multilayer dielectric grating pillar-removal damage induced by a picosecond laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2022, e42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The associations between depressive symptoms, functional impairment, and quality of life, in patients with major depression: undirected and Bayesian network analyses
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2022, pp. 6446-6458
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vibration-induced ‘anti-gravity’ tames thermal turbulence at high Rayleigh numbers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 951 / 25 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2022, A13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of Eliminating the US–China Trade Dispute Tariffs
-
- Journal:
- World Trade Review / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2022, pp. 212-231
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Suppression of flow reversals via manipulating corner rolls in plane Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 946 / 10 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2022, A44
-
- Article
- Export citation
In-situ TEM and Spectroscopy Studies of Nanoscale Perpendicular Magnetic Tunnel Junction
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 838-840
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Multiple molecular characteristics of circulating enterovirus types among paediatric hand, foot and mouth disease patients after EV71 vaccination campaign in Wuxi, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2022, e98
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation