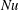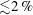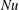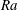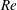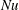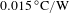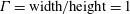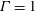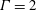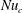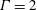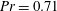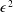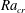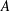68 results
Shakespeare and Accentism. Adele Lee, ed. Routledge Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Literature. New York: Routledge, 2021. x + 222 pp. $170.
-
- Journal:
- Renaissance Quarterly / Volume 76 / Issue 2 / Summer 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2023, pp. 793-794
- Print publication:
- Summer 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary inflammatory index, inflammation biomarkers and preeclampsia risk: a hospital-based case–control study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2022, pp. 1528-1536
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Currency substitution as an automatic stabilizer
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 27 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2021, pp. 432-455
-
- Article
- Export citation
X-ray powder diffraction data for rivaroxaban, C19H18ClN3O5S
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2021, pp. 40-42
-
- Article
- Export citation
A preliminary study of Badimia Vězda (Ramalinaceae) in East Asia
-
- Journal:
- The Lichenologist / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 327-334
- Print publication:
- July 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Midazolam for conscious sedation in transcatheter device closure of atrial septal defects guided solely by transthoracic echocardiography
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2021, pp. 282-286
-
- Article
- Export citation
PROGRESSIVE TAXATION AND MACROECONOMICS (IN)STABILITY UNDER HOUSEHOLD HETEROGENEITY
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 26 / Issue 7 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2021, pp. 1891-1922
-
- Article
- Export citation
EQUILIBRIUM INDETERMINACY, ENDOGENOUS ENTRY AND EXIT, AND INCREASING RETURNS TO SPECIALIZATION
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 26 / Issue 7 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2021, pp. 1756-1774
-
- Article
- Export citation
Training to Improve Clinical Specimen Collection and Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Diagnostics and Surveillance in Ethiopia
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2020, p. s414
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effects of dairy products, calcium and vitamin D on ovarian cancer risk: a meta-analysis of twenty-nine epidemiological studies
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2020, pp. 1001-1012
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
On non-Oberbeck–Boussinesq effects in Rayleigh–Bénard convection of air for large temperature differences
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 889 / 25 April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2020, A10
-
- Article
- Export citation
The psychological typhoon eye effect in responses to terrorism
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology / Volume 14 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2020, e21
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between dietary patterns and chronic kidney disease in a middle-aged Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 23 / Issue 6 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 October 2019, pp. 1058-1066
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Calibration and verification of streaked optical pyrometer system used for laser-induced shock experiments
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2019, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Polygenic effects of schizophrenia on hippocampal grey matter volume and hippocampus–medial prefrontal cortex functional connectivity
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 216 / Issue 5 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 June 2019, pp. 267-274
- Print publication:
- May 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fabrication of kW-level chirped and tilted fiber Bragg gratings and filtering of stimulated Raman scattering in high-power CW oscillators
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2019, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Corrosion-resistant fluoridated Ca–Mg–P composite coating on magnesium alloys prepared via hydrothermal assisted sol–gel process
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 33 / Issue 22 / 28 November 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2018, pp. 3793-3800
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flow reversals in two-dimensional thermal convection in tilted cells
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 849 / 25 August 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 June 2018, pp. 355-372
-
- Article
- Export citation
Linear and weakly nonlinear analysis of Rayleigh–Bénard convection of perfect gas with non-Oberbeck–Boussinesq effects
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 845 / 25 June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2018, pp. 141-169
-
- Article
- Export citation
A NOTE ON NOMINAL GDP TARGETING AND MACROECONOMIC (IN)STABILITY
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 23 / Issue 8 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2018, pp. 3483-3508
-
- Article
- Export citation