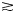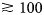342 results
Harmonizing human-AI synergy: behavioral science in AI-integrated design
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 4 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, pp. 2287-2296
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A proposal for an updated and revised stratigraphical framework of the Miocene in the Achterhoek (eastern Netherlands)
-
- Journal:
- Netherlands Journal of Geosciences / Volume 103 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Disentangling potential causal effects of educational duration on well-being, and mental and physical health outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 7 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2023, pp. 1403-1418
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Radiofrequency ice dielectric measurements at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Socio-economic status and other potential risk factors for language development in the first year of life
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Child Language , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ground penetrating radar in temperate ice: englacial water inclusions as limiting factor for data interpretation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
15 - Solving Larger Seismic Inverse Problems with Smarter Methods
- from Part III - ‘Solid’ Earth Applications: From the Surface to the Core
-
-
- Book:
- Applications of Data Assimilation and Inverse Problems in the Earth Sciences
- Published online:
- 20 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 06 July 2023, pp 239-251
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Virasoro constraints for moduli spaces of sheaves on surfaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2023, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
6 - Transnational dynamics of family reunification: reassembling social work with refugees in Belgium
-
-
- Book:
- Migration and Social Work
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 17 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 16 January 2023, pp 95-111
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 14 - The Matter of Absence
-
-
- Book:
- Samuel Beckett's Poetry
- Published online:
- 15 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 22 December 2022, pp 219-234
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 8 - The Intertextual Condition
- from Part II - Fragment and Frame
-
-
- Book:
- The New Joyce Studies
- Published online:
- 01 September 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 September 2022, pp 123-137
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Probing Atom Dynamics in Excited Nanocrystals
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2128-2129
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
3D Atom Dynamics in Pt-NiO Nanocrystals
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2232-2234
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
How do the determinants of exclusive breast-feeding change over time? A multi-survey quasi-longitudinal study in Lao People’s Democratic Republic
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 9 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2022, pp. 2380-2394
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generalizability in mixed models: Lessons from corpus linguistics
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 45 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2022, e34
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modulating Electron Beam–Sample Interactions in Imaging and Diffraction Modes by Dose Fractionation with Low Dose Rates
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2021, pp. 1420-1430
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A new generic method to extract stoichiometric and dynamic information from the exit-wave for thin sample
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 2314-2316
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Observing atomic resolution dynamics of soft materials with controlling dose rate
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 2124-2126
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The relationship between cognitive functioning and psychopathology in patients with psychiatric disorders: a transdiagnostic network analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2021, pp. 476-485
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lexicon or grammar? Using memory-based learning to investigate the syntactic relationship between Belgian and Netherlandic Dutch
-
- Journal:
- Natural Language Engineering / Volume 28 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2021, pp. 649-667
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation