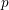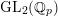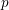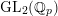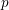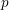54 results
Components of moduli stacks of two-dimensional Galois representations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2024, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clinical outcomes with paliperidone palmitate 3-monthly injection as monotherapy: observational 3-year follow-up of patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A tool for safer prescribing in vulnerable adults: the continuing development of the Medichec app and website
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Bulletin , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clinical impact of reducing the frequency of clozapine monitoring: controlled mirror-image cohort study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 223 / Issue 2 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 382-388
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A qualitative process evaluation of social recovery therapy for enhancement of social recovery in first-episode psychosis (SUPEREDEN3)
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 51 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2022, pp. 133-145
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Demystifying the pathway of assessment and treatment for bipolar disorder – utilising co-production and algorithms to personalise the approach
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue S1 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 June 2021, p. S150
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Demystifying the pathway of assessment and treatment for bipolar disorder – utilising co-production and algorithms to personalise the approach
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue S1 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 June 2021, pp. S149-S150
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The IALS Library Transformed!
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 October 2021, pp. 69-73
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
SLS/BIALL Academic Law Library Survey 2017/2018
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 19 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2019, pp. 142-160
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 15 - Biogeographic Comparisons of Pattern and Process on Intertidal Rocky Reefs of New Zealand and South-Eastern Australia
-
-
- Book:
- Interactions in the Marine Benthos
- Published online:
- 07 September 2019
- Print publication:
- 29 August 2019, pp 391-413
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The Effect of Natural Disasters on Cancer Care: A Systematic Review
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 34 / Issue s1 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2019, p. s48
- Print publication:
- May 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
SLS/BIALL Academic Law Library Survey 2016/2017
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 18 / Issue 3 / September 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2018, pp. 171-189
- Print publication:
- September 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
IALS@70: the Growth of the IALS Library and its Development of Digital Initiatives for the UK Legal Community
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 18 / Issue 1 / March 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2018, pp. 35-40
- Print publication:
- March 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
SLS/BIALL Academic Law Library Survey 2015/2016
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2018, pp. 245-264
- Print publication:
- December 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Patching and the
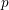 $p$
-adic Langlands program for
$p$
-adic Langlands program for
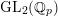 $\operatorname{GL}_{2}(\mathbb{Q}_{p})$
$\operatorname{GL}_{2}(\mathbb{Q}_{p})$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 154 / Issue 3 / March 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2017, pp. 503-548
- Print publication:
- March 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Improving the effectiveness of psychotherapy in two public hospitals in Nairobi
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych International / Volume 14 / Issue 3 / August 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2018, pp. 64-66
- Print publication:
- August 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Guest Editorial
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 17 / Issue 2 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2017, p. 74
- Print publication:
- June 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
SLS/BIALL Academic Law Library Survey 2014/2015
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 16 / Issue 4 / December 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2016, pp. 239-257
- Print publication:
- December 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Guest Editorial
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 16 / Issue 2 / June 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2016, pp. 58-59
- Print publication:
- June 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
SLS/BIALL Academic Law Library Survey 2013/2014
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 15 / Issue 4 / December 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2015, pp. 264-282
- Print publication:
- December 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation