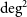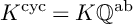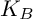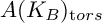1201 results
Intestinal parasite infection and sanitation in medieval Leiden, the Low Countries
-
- Journal:
- Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
B.6 Long-term risk of subsequent stroke after transient ischemic attack or minor stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Swapping white for high-fibre bread exceeds fibre target and improves microbiome diversity
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 83 / Issue OCE1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2024, E15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Seasonality in regional brain glucose metabolism
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
RG-CAT: Detection pipeline and catalogue of radio galaxies in the EMU pilot survey
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, e027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A multisystem model for understanding stress and adaptation in ethnically and racially diverse youth
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Research into land atmosphere interactions supports the sustainable development agenda
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 7 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A five-year quasi-experimental study to evaluate the impact of empiric antibiotic order sets on antibiotic use metrics among hospitalized adult patients
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 609-617
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Aflatoxin B1 Sorption and Safety of Dietary Sodium Bentonite in Sprague-Dawley Rats
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 165-181
-
- Article
- Export citation
NovaSil Clay for the Protection of Humans and Animals from Aflatoxins and Other Contaminants
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / 15 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 99-110
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis of Cu-Containing Layered Double Hydroxides with a Narrow Crystallite-Size Distribution
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 51 / Issue 5 / October 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 566-569
-
- Article
- Export citation
9 Serum Neurofilament is Associated with Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in Chronic Mild-Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
88 Social Cognition and Information Processing Speed in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis and Co-Morbid Diabetes: An Interim Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 79-80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
4 Associations Between Glycemia and Cognitive Performance in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) using Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Ecological Momentary Assessment (EMA)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 792-793
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
25 Associations between Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging, Tau, and Cognitive Outcomes in TBI
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 134-135
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Nonlinear interaction of Alfvénic instabilities and turbulence via the modification of the equilibrium profiles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, 905890602
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anatomic considerations in the management of complete atrioventricular canal
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 October 2023, pp. 754-758
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Geoarchaeology and Coastal Morphodynamics of Harbor Key (8MA15): Indigenous Persistence at a Partially Inundated Native Shell Mound Complex in Tampa Bay, Florida
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 88 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 531-553
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON THE ESSENTIAL TORSION FINITENESS OF ABELIAN VARIETIES OVER TORSION FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 253 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 91-127
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Transdiagnostic indicators predict developmental changes in cognitive control resting-state networks
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation