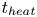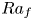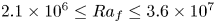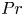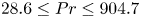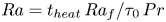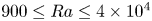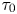5809 results

Web3
- Blockchain, the New Economy, and the Self-Sovereign Internet
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- August 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 August 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
The design and optimization methods towards 10 kW high beam quality fiber laser based on counter tandem pumping scheme
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Neuroimaging evidence dissociates forced and free language selection during bilingual speech production
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protecting Your Friends: The Role of Connections in Division Manager Careers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 1-58
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nutritional programming of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae by dietary vegetable oil: effects on growth performance, lipid metabolism and antioxidant capacity – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prediction of wrinkle patterns in tensioned thin-film structures containing rigid elements
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genetic Causal Relationship Between Alanine Aminotransferase Levels and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Mendelian Randomization Analysis Based on Two Samples
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
ISOCHRONOUS CENTERS AND FLAT FINSLER METRICS (I)
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Phylogenetic trends in TZ staining analysis of six deep dormancy seeds
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Survey of Spirometra erinaceieuropaei in frogs in Taiwan and its experimental infection in cats
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 74 / Issue 2 / June 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 173-176
-
- Article
- Export citation
Automatic extrinsic calibration for structured light camera and repetitive LiDARs
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Formation and evolution of laminar thermal structures: correlation to the thermal boundary layer and effects of heating time
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, A60
-
- Article
- Export citation
259 Eighty-six-fold increase in HIV diagnosis with “Opt-out” Screening: Frontlines of Communities in the U.S. (FOCUS) Program in the UHealth Tower (UHT) Emergency Department (ED) - path to eliminate HIV transmission in the U.S.
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, pp. 78-79
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
302 Diagnostic Evidence Gauge of Spatial Transcriptomics (DEGAS-ST): Using transfer learning to map clinical data to spatial transcriptomics in prostate cancer
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
23 AHA’s Essential Eight: Opportunities for Preventive Care among Adults with Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, pp. 6-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
337 Cellular senescence contributes to inflammation and disease progression in an animal model of multiple sclerosis
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 102
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
New material of the zosterophyllopsid Gosslingia from the Lower Devonian of Guizhou, southwestern China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Influence of Mn2+ and pH on the Formation of Iron Oxides from Ferrous Chloride and Ferrous Sulfate Solutions
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 37 / Issue 5 / October 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 451-458
-
- Article
- Export citation