Book contents
- Decision-Making in Orthopedic and Regional AnesthesiologyA Case-Based Approach
- Decision-Making in Orthopedic and Regional Anesthesiology
- Copyright page
- Contents
- List of contributors
- Preface
- Section 1 General considerations in regional anesthesia
- Section 2 Special patient considerations
- Section 3 Total joint replacements
- Section 4 Orthopedic trauma
- Section 5 Sports medicine and hand surgery
- Chapter 30 Rotator cuff repair
- Chapter 31 Anterior cruciate ligament repair
- Chapter 32 Hand surgery and choosing appropriate anesthetic techniques
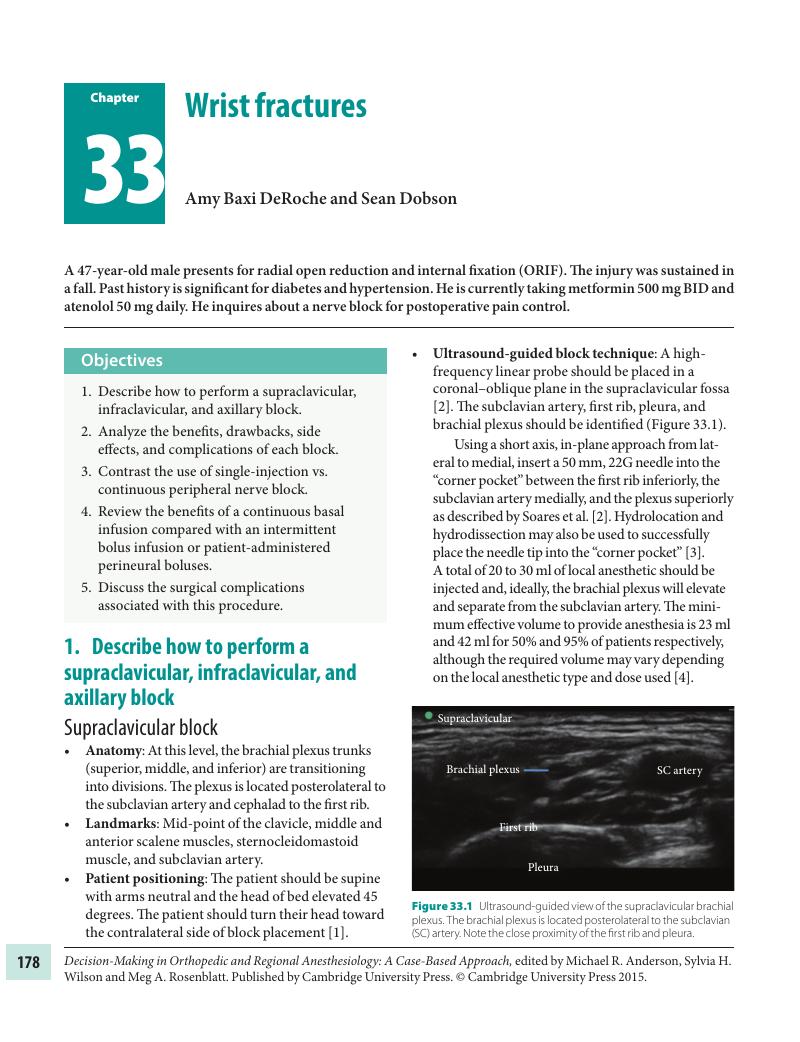
- Chapter 33 Wrist fractures
- Chapter 34 Analgesia for iliac crest bone graft
- Index
- References
Chapter 33 - Wrist fractures
from Section 5 - Sports medicine and hand surgery
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 October 2015
- Decision-Making in Orthopedic and Regional AnesthesiologyA Case-Based Approach
- Decision-Making in Orthopedic and Regional Anesthesiology
- Copyright page
- Contents
- List of contributors
- Preface
- Section 1 General considerations in regional anesthesia
- Section 2 Special patient considerations
- Section 3 Total joint replacements
- Section 4 Orthopedic trauma
- Section 5 Sports medicine and hand surgery
- Chapter 30 Rotator cuff repair
- Chapter 31 Anterior cruciate ligament repair
- Chapter 32 Hand surgery and choosing appropriate anesthetic techniques
- Chapter 33 Wrist fractures
- Chapter 34 Analgesia for iliac crest bone graft
- Index
- References
Summary
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Decision-Making in Orthopedic and Regional AnesthesiologyA Case-Based Approach, pp. 178 - 183Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2015



