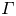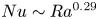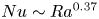388 results
Effectiveness of Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition and Subjective Global Assessment for diagnosing malnutrition and predicting wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
The role of the cytochrome P450 superfamily in the skin
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trauma diagnostic-related target proteins and their detection techniques
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reflection of a centred compression wave
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 March 2024, A3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mineralogy of Dickite and Nacrite From Northern Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 49 / Issue 6 / December 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 586-595
-
- Article
- Export citation
Kaolin Mineralogy of Clays in Paleosol Profiles on the Late-Miocene Sediments in Penghu Islands (Pescadores), Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / February 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transverse magnetic field effects on the high-voltage pulsed discharge plasma in helium
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, 905900115
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary factors and the risk of atopic dermatitis: a Mendelian randomisation study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 11 / 14 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, pp. 1873-1882
- Print publication:
- 14 June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Milk proteomic analysis reveals differentially expressed proteins in high-yielding and low-yielding Guanzhong dairy goats at peak lactation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 91 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 31-37
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dry storage alters intraspecific variation in phenotypic traits at early life stages: evidence from a dominant alpine meadow species
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research / Volume 33 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, pp. 203-212
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Kaolin Minerals from Chinmen Island (Quemoy)
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 130-137
-
- Article
- Export citation
Downregulated miR-150-5p in the Tissue of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Seasonal Variation in the Mineralogy of the Suspended Particulate Matter of the Lower Changjiang River at Nanjing, China
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 5 / October 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 691-706
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of the SiO2/Al2O3 Molar Ratio on the Microstructure and Properties of Clay-based Geopolymers: A Comparative Study of Kaolinite-based and Halloysite-based Geopolymers
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 882-902
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis of the Effect of β-Elemene on Colorectal Cancer from the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Critical Textural Evolution Study of Zerovalent Iron/Montmorillonite Nanosized Heterostructures Under Various Iron Loadings
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 490-500
-
- Article
- Export citation
Protective factors for children with autism spectrum disorder during COVID-19-related strict lockdowns: a Shanghai autism early developmental cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 6 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 1102-1112
-
- Article
- Export citation
Strong coupling of flow structure and heat transport in liquid metal thermal convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, A21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Gray matter atrophy is constrained by normal structural brain network architecture in depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 7 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 1318-1328
-
- Article
- Export citation
Changing trends in the global burden of mental disorders from 1990 to 2019 and predicted levels in 25 years
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation