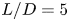73 results
Vortex dynamics and boundary layer transition in flow around a rectangular cylinder with different aspect ratios at medium Reynolds number
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 982 / 10 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, A5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Protective factors for children with autism spectrum disorder during COVID-19-related strict lockdowns: a Shanghai autism early developmental cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 6 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 1102-1112
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of illustration art combined with Compound sea snake capsule on Alzheimer
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Bidirectional relations between altruistic tendency and benign/malicious envy among adolescents: A longitudinal study and weekly diary study
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2023, pp. 765-773
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characteristics of patients with SARS-COV-2 PCR re-positivity after recovering from COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2023, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Longitudinal relations among family dysfunction, depressive symptoms, and cyberbullying involvement in Chinese early adolescents: Disentangling between- and within-person associations
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2022, pp. 395-403
-
- Article
- Export citation
Three-dimensional vortex dynamics and transitional flow induced by a circular cylinder placed near a plane wall with small gap ratios
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 953 / 25 December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2022, A2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Understanding guilt-related interpersonal dysfunction in obsessive-compulsive personality disorder through computational modeling of two social interaction tasks
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2022, pp. 5569-5581
-
- Article
- Export citation
Suing the State: Relative Deprivation and Peasants’ Resistance in Land Expropriation in China
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 251 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 798-821
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Room Temperature Néel-type Skyrmions in a van der Waals Ferromagnet Revealed by Lorentz 4D-STEM
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 1710-1712
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The stability analysis of a 2D Keller–Segel–Navier–Stokes system in fast signal diffusion
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2022, pp. 160-209
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nomograms including the controlling nutritional status score in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial chemoembolisation for prediction survival: a retrospective analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2021, pp. 1966-1974
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Influencing mechanisms of lifestyle and dietary factors on chronic diseases among community residents: updated evidence in Shanghai, China
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 October 2021, pp. 1233-1245
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Antennal transcriptome analysis and candidate olfactory genes in Crematogaster rogenhoferi
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 111 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2021, pp. 464-475
-
- Article
- Export citation
EB1 Is Essential for Spindle Formation and Chromosome Alignment During Oocyte Meiotic Maturation in Mice
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2021, pp. 385-391
- Print publication:
- April 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Blunted reward prediction error signals in internet gaming disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 11 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2020, pp. 2124-2133
-
- Article
- Export citation
Managing herbicide resistance in China
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2020, pp. 4-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of dietary methionine on growth performance, muscle nutritive deposition, muscle fibre growth and type I collagen synthesis of on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 3 / 14 August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2020, pp. 321-336
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tackling the mental health burden of frontline healthcare staff in the COVID-19 pandemic: China's experiences
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 11 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2020, pp. 1955-1956
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation