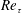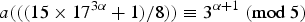70 results
Progressive grey matter atrophy in adolescents with major depressive disorder revealed by causal structural covariance network
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, pp. S190-S191
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
New mock theta functions and formulas for basic hypergeometric series
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, pp. 868-896
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigating particle acceleration dynamics in interpenetrating magnetized collisionless super-critical shocks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, 915890101
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acceleration of 60 MeV proton beams in the commissioning experiment of the SULF-10 PW laser
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploiting 3D Variational Autoencoders for Interactive Vehicle Design
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2022, pp. 1747-1756
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Decreased nasal nitric oxide levels: a potential marker of decreased olfactory discrimination in chronic rhinosinusitis
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 136 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2021, pp. 419-426
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
A repairable carbon nanotube web-based electro-thermal heater and damage sensor for aerospace applications
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 125 / Issue 1292 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 May 2021, pp. 1833-1843
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of the frequency of mutation genes in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) strains in Beijing, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2021, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Altered coupling of default-mode, executive-control and salience networks in Internet gaming disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 45 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, pp. 114-120
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the detection of internal interfacial layers in turbulent flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 872 / 10 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2019, pp. 198-217
-
- Article
- Export citation
Infinite families of congruences modulo 5 and 7 for the cubic partition function
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 149 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2019, pp. 1189-1205
- Print publication:
- October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Differential prevalence and correlates of whole blood Epstein–Barr virus DNA between HIV-positive and HIV-negative men who have sex with men in Shanghai, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 145 / Issue 11 / August 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2017, pp. 2330-2340
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Phenotypic and molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in slaughterhouse pig-related workers and control workers in Guangdong Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 145 / Issue 9 / July 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2017, pp. 1843-1851
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Glacial Stage Ice-Core Records from the Subtropical Dunde Ice Cap, China
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology / Volume 14 / 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 288-297
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
15N-Leucine: Health benefits, applications and issues related to ileal endogenous amino acid losses in poultry
-
- Journal:
- World's Poultry Science Journal / Volume 73 / Issue 1 / March 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2017, pp. 145-162
- Print publication:
- March 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Load Detection of Functionally Graded Material Based on Coherent Gradient Sensing Method
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Mechanics / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2016, pp. 299-310
- Print publication:
- June 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Common pattern of gray-matter abnormalities in drug-naive and medicated first-episode schizophrenia: a multimodal meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 47 / Issue 3 / February 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2016, pp. 401-413
-
- Article
- Export citation
Role of microRNA508-3p in melanogenesis by targeting microphthalmia transcription factor in melanocytes of alpaca
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation