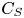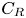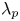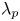493 results
Integral methods for friction decomposition and their extensions to rough-wall flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 985 / 25 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, A46
-
- Article
- Export citation
Precise mode control of mid-infrared high-power laser diode using on-chip advanced sawtooth waveguide designs
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Phylogenetic trends in TZ staining analysis of six deep dormancy seeds
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Instrumental Guanxi Culture and Inbound Urban Migration in China: A Prefecture-level Analysis Using Online Search Data
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
- Export citation
The p factor outweighs the specific internalizing factor in predicting recurrences of adolescent depression
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2024, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Kaolin Mineralogy of Clays in Paleosol Profiles on the Late-Miocene Sediments in Penghu Islands (Pescadores), Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / February 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring the Barriers and Facilitators of Mask-Wearing Behavior During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Taiwan, the United States, the Netherlands, and Haiti: A Qualitative Study
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary factors and the risk of atopic dermatitis: a Mendelian randomisation study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 11 / 14 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, pp. 1873-1882
- Print publication:
- 14 June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
P199: Cluster analysis dissecting cognitive deficits in older adults with major depressive disorder and the association between neurofilament light chain
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 188-189
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
AMS 14C DATING AND STABLE ISOTOPE ANALYSIS ON AN 8-KYR OYSTER SHELL FROM TAIPEI BASIN: SEA LEVEL AND SST CHANGES
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Alpha-Particle Generation from H-11B Fusion Initiated by Laser-Accelerated Boron Ions
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of Dietary Palygorskite Supplementation on Cecal Microbial Community Structure and the Abundance of Antibiotic-Resistant Genes in Broiler Chickens Fed With Chlortetracycline
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 205-216
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structural Controls on the Catalytic Polymerization of Hydroquinone by Birnessites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 525-537
-
- Article
- Export citation
Downregulated miR-150-5p in the Tissue of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Charge State of Protons with 90 and 100 keV Energies Decelerated in Hydrogen Plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Smectite Dehydration Model in a Shallow Sedimentary Basin: Model Development
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / February 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 55-70
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation Of Zinc-Bearing Palygorskite Effects on Growth Performance, Nutrient Retention, Meat Quality, and Zinc Accumulation in Blunt Snout Bream Megalobrama Amblycephala
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 274-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Evaluation of the Supplementation of Dietary-Modified Palygorskite on Growth Performance, Zearalenone Residue, Serum Metabolites, and Antioxidant Capacities in Broilers Fed a Zearalenone-Contaminated Diet
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 6 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 474-484
-
- Article
- Export citation
8 Effects of Birthweight and Home Environment on Cognitive Executive Functions at Preschool-Age of VLBW / ELBW Preterm Children with Normal Early Development
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 618-619
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
44 Develop A Social Perception Test: The Psychometric Properties of Child's version Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test in Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 831-832
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation